1-(1-Hydr-oxy-9H-carbazol-2-yl)-3-methyl-but-2-en-1-one
- PMID: 21579731
- PMCID: PMC2979736
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810000322
1-(1-Hydr-oxy-9H-carbazol-2-yl)-3-methyl-but-2-en-1-one
Abstract
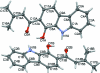
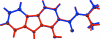
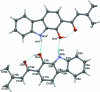
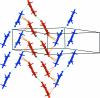
The title compound, C(17)H(15)NO(2), was prepared as one of two products of the AlCl(3)/POCl(3)-catalysed reaction of 9-carbazol-1-ol with 3,3-dimethyacrylic acid. It crystallizes with two crystallographically independent mol-ecules, A and B, which are virtually superimposable but not related by any translational or other pseudosymmetry. Both independent mol-ecules are almost planar [r.m.s. deviations from planarity = 0.053 (1) and 0.079 (1) Å in A and B, respectively] and contain an intramolecular O-H⋯O hydrogen bond. Each type of mol-ecules is connected via pairs of N-H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming centrosymmetric A(2) and B(2) dimers which are, in turn, arranged in offset π-stacks extending along the a-axis direction. The offset of the dimers and the tilt angle of the mol-ecules allows the formation of alternating C-H⋯π inter-actions between A and B mol-ecules of parallel stacks.
Figures

References
-
- Bruker (2007). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Chakraborty, D. P. (1993). The Alkaloids, edited by A. Brossi, Vol. 44, pp. 257–282. New York: Academic Press.
-
- Kavitha, C. & Rajendra Prasad, K. J. (2003a). J. Chem. Res. (S), pp. 606–607.
-
- Kavitha, C. & Rajendra Prasad, K. J. (2003b). J. Chem. Res. (M), pp. 1025–1036.
-
- Knölker, H. J. & Reddy, K. R. (2002). Chem. Rev.102, 4303–4428. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
