tert-Butyl 2-methyl-2-(4-nitro-benzo-yl)propanoate
- PMID: 21579899
- PMCID: PMC2979732
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810003119
tert-Butyl 2-methyl-2-(4-nitro-benzo-yl)propanoate
Abstract
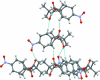
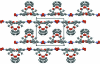
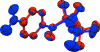
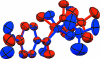
The title compound, C(15)H(19)NO(5), is bent with a dihedral angle of 61.8 (2)° between the mean planes of the benzene ring and a group encompassing the ester functionality (O=C-O-C). The dihedral angle of 0.8 (2)° between the mean planes of the nitro group and the benzene ring indicates near coplanarity. In the crystal, each mol-ecule is linked to four adjacent mol-ecules by weak C-H⋯O hydrogen-bonding inter-actions. Both benzene H atoms ortho to the ketone O atom form C-H⋯O hydrogen bonds with the keto O atoms of two neighboring mol-ecules (of the keto and ester groups, respectively), and the two other inter-actions involve the H atoms from a methyl group of the dimethyl residue, displaying C-H⋯O inter-actions with the O atoms of the nitro groups. These four inter-actions for each mol-ecule lead to the formation of two-dimensional sheets with a hydro-philic inter-ior, held together by weak hydrogen-bonded inter-actions, and a hydro-phobic exterior composed of protruding methyl groups which interst-ack with the methyl groups in adjacent sheets.
Figures
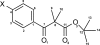




References
-
- Alemán, J., Reyes, E., Richter, B., Overgaard, J. & Jørgensen, K. A. (2007). Chem. Commun. pp. 3921–3923. - PubMed
-
- Burla, M. C., Caliandro, R., Camalli, M., Carrozzini, B., Cascarano, G. L., De Caro, L., Giacovazzo, C., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (2005). J. Appl. Cryst.38, 381–388.
-
- Elsner, P., Bernardi, L., Salla, G. D., Overgaard, J. & Jørgensen, K. A. (2008). J. Am. Chem. Soc.130, 4897–4905. - PubMed
-
- Enraf–Nonius (1994). CAD-4 EXPRESS Enraf–Nonius, Delft, The Netherlands.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
