4-(Dimethyl-amino)phenyl ethynyl telluride
- PMID: 21582534
- PMCID: PMC2968982
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809009404
4-(Dimethyl-amino)phenyl ethynyl telluride
Abstract
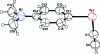
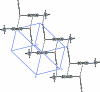
The title compound, C(10)H(11)NTe, is the first organyl ethynyl telluride, R-Te-C C-H, to be structurally characterized. In the L-shaped mol-ecule, the aryl moiety, viz. Me(2)NC(6)H(4)Te, is almost perpendicular to the Te-C C-H fragment. The Te-Csp(2) bond [2.115 (3) Å] is significantly longer than the Te-Csp bond [2.041 (4) Å]. The Te-C C group is approximately linear [Te-C-C = 178.5 (4)° and C C = 1.161 (5) Å], while the coordination at the Te atom is angular [C-Te-C = 95.92 (14)°]. In the crystal structure, there are Csp-H⋯N hydrogen bonds which are perpendicular to the CNMe(2) group; the N atom displays some degree of pyramidalization. Centrosymmetrically related pairs of mol-ecules are linked by Te⋯π(ar-yl) inter-actions, with Te⋯Cg = 3.683 (4) Å and Csp-Te⋯Cg = 159.1 (2)° (Cg is the centroid of the benzene ring). These inter-actions lead to the formation of zigzag ribbons which run along c and are approximately parallel to (110).
Figures
References
-
- Brandsma, L. (1988). Preparative Acetylenic Chemistry, p. 27. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
-
- Bruker (2001). SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Bruker (2002). SMART Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Dabdoub, M. J., Begnini, M. L. & Guerrero, P. G. Jr (1998). Tetrahedron, 54, 2371–2400.
-
- Farran, J., Torres-Castellanos, L., Alvarez-Larena, A., Piniella, J. F. & Capparelli, M. V. (2002). J. Organomet. Chem.654, 91–99.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials