Ethyl-enediammonium dichloride
- PMID: 21583203
- PMCID: PMC2969764
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809018327
Ethyl-enediammonium dichloride
Abstract
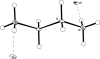
The title ionic compound, C(2)H(10)N(2) (2+)·2Cl(-), crystallizes with a center of symmetry within the cation. Each of the positively charged ammonium ends of the mol-ecule is trigonally hydrogen bonded to three different chloride counter-ions, while each of the chloride ions is trigonally hydrogen bonded to three different ethyl-enediammonium cations. The hydrogen-bonding network leads to stabilization of the structure.
Figures

References
-
- Bruker (2005). SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Bruker (2006). APEX2 Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Kotti, S. R. S. S., Timmons, C. & Li, G. (2006). Chem. Biol. Drug Des.67, 101–114. - PubMed
-
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2001). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
-
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
