Deciphering the key molecular and cellular events in neutrophil transmigration during acute inflammation
- PMID: 21584186
- PMCID: PMC3089884
- DOI: 10.6026/97320630006111
Deciphering the key molecular and cellular events in neutrophil transmigration during acute inflammation
Abstract
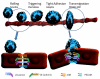
Recruitment of leukocytes circulating in our blood to the sites of infection or tissue damage is the key phenomenon in the acute inflammatory response(s). Among the leukocytes, neutrophils are primarily recruited into the areas of acute inflammation. When neutrophils interact with activated endothelium of the blood vessels, they become migratory and cross the endothelial layer of the blood vessel wall in a process called as leukocyte extravasation. Identifying and understanding the gene regulation of this extravasation phenomenon is one of the key objective of biomedical research aimed at ameliorating or alleviating the symptoms of various diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, asthma, anaphylaxis, atherosclerosis, ulcerative colitis etc., that are exacerbated by inappropriate inflammatory stimuli. Here, we decipher and discuss the key genes implicated in the leukocyte transmigration using the acute inflammation model called as the Dextran Sulphate Sodium (DSS) induced Colitis in mice as a classic paradigm.
Keywords: Acute Inflammation; Colonic Epithelium; DSS Colitis; Extravasation; Leukocytes; Neutrophils Endothelium; Transmigration.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Activation of endothelial extracellular signal-regulated kinase is essential for neutrophil transmigration: potential involvement of a soluble neutrophil factor in endothelial activation.J Immunol. 2003 Dec 1;171(11):6097-104. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.11.6097. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14634124
-
Neutrophil transendothelial migration hotspots - mechanisms and implications.J Cell Sci. 2021 Apr 1;134(7):jcs255653. doi: 10.1242/jcs.255653. J Cell Sci. 2021. PMID: 33795378 Review.
-
CD40-CD40 ligand mediates the recruitment of leukocytes and platelets in the inflamed murine colon.Gastroenterology. 2007 Mar;132(3):955-65. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.12.027. Epub 2006 Dec 17. Gastroenterology. 2007. PMID: 17324402
-
Deficiency of Dietary Fiber Modulates Gut Microbiota Composition, Neutrophil Recruitment and Worsens Experimental Colitis.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 23;12:619366. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.619366. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33708211 Free PMC article.
-
Heparan sulphate as a regulator of leukocyte recruitment in inflammation.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2015;16(1):77-86. doi: 10.2174/1573402111666150213165054. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2015. PMID: 25692849 Review.
Cited by
-
CD4+CD29+T cells are blamed for the persistent inflammatory response in ulcerative colitis.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Mar 1;8(3):2627-37. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26045768 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling the pasture-associated severe equine asthma bronchoalveolar lavage fluid proteome identifies molecular events mediating neutrophilic airway inflammation.Vet Med (Auckl). 2019 May 2;10:43-63. doi: 10.2147/VMRR.S194427. eCollection 2019. Vet Med (Auckl). 2019. PMID: 31119093 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-33 exacerbates acute colitis via interleukin-4 in mice.Immunology. 2013 Sep;140(1):70-7. doi: 10.1111/imm.12111. Immunology. 2013. PMID: 23582173 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of extracellular matrix proteins on neutrophil-endothelial interaction--a roadway to multiple therapeutic opportunities.Yale J Biol Med. 2012 Jun;85(2):167-85. Epub 2012 Jun 25. Yale J Biol Med. 2012. PMID: 22737047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disease associated cellular machinery in anaphylaxis - And the de novo paradigm shift.Bioinformation. 2015 Jan 30;11(1):43-6. doi: 10.6026/97320630011043. eCollection 2015. Bioinformation. 2015. PMID: 25780280 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
