Conflicting effects of excitatory synaptic and electric coupling on the dynamics of square-wave bursters
- PMID: 21584773
- PMCID: PMC3190594
- DOI: 10.1007/s10827-011-0340-1
Conflicting effects of excitatory synaptic and electric coupling on the dynamics of square-wave bursters
Abstract
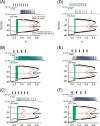
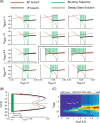
Using two-cell and 50-cell networks of square-wave bursters, we studied how excitatory coupling of individual neurons affects the bursting output of the network. Our results show that the effects of synaptic excitation vs. electrical coupling are distinct. Increasing excitatory synaptic coupling generally increases burst duration. Electrical coupling also increases burst duration for low to moderate values, but at sufficiently strong values promotes a switch to highly synchronous bursts where further increases in electrical or synaptic coupling have a minimal effect on burst duration. These effects are largely mediated by spike synchrony, which is determined by the stability of the in-phase spiking solution during the burst. Even when both coupling mechanisms are strong, one form (in-phase or anti-phase) of spike synchrony will determine the burst dynamics, resulting in a sharp boundary in the space of the coupling parameters. This boundary exists in both two cell and network simulations. We use these results to interpret the effects of gap-junction blockers on the neuronal circuitry that underlies respiration.
Figures



References
-
- Bertram R, Butte MJ, Kiemel T, Sherman A. Topological and phenomenological classification of bursting oscillations. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology. 1995;57:413–439. - PubMed
-
- Best J, Borisyuk A, Rubin J, Terman D, Wechselberger M. The dynamic range of bursting in a model respiratory pacemaker network. SIAM Journal on Applied Dynamical Systems. 2005;4:1107–1139.
-
- Bou-Flores C, Berger AJ. Gap junctions and inhibitory synapses modulate inspiratory motoneuron synchronization. Journal of Neurophysiology. 2001;85:1543–1551. - PubMed
-
- Butera RJ, Jr., Rinzel J, Smith JC. Models of respiratory rhythm generation in the pre-Botzinger complex. I. Bursting pacemaker neurons. Journal of Neurophysiology. 1999;82:382–397. - PubMed
-
- De Vries G, Sherman A, Zhu HR. Diffusively coupled bursters: effects of cell heterogeneity. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology. 1998;60:1167–1200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

