Three-dimensional echocardiography for left ventricular quantification: fundamental validation and clinical applications
- PMID: 21584798
- PMCID: PMC3189315
- DOI: 10.1007/s12471-011-0160-y
Three-dimensional echocardiography for left ventricular quantification: fundamental validation and clinical applications
Abstract
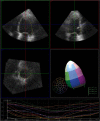
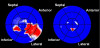
One of the earliest applications of clinical echocardiography is evaluation of left ventricular (LV) function and size. Accurate, reproducible and quantitative evaluation of LV function and size is vital for diagnosis, treatment and prediction of prognosis of heart disease. Early three-dimensional (3D) echocardiographic techniques showed better reproducibility than two-dimensional (2D) echocardiography and narrower limits of agreement for assessment of LV function and size in comparison to reference methods, mostly cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging, but acquisition methods were cumbersome and a lack of user-friendly analysis software initially precluded widespread use. Through the advent of matrix transducers enabling real-time three-dimensional echocardiography (3DE) and improvements in analysis software featuring semi-automated volumetric analysis, 3D echocardiography evolved into a simple and fast imaging modality for everyday clinical use. 3DE provides the possibility to evaluate the entire LV in three spatial dimensions during the complete cardiac cycle, offering a more accurate and complete quantitative evaluation the LV. Improved efficiency in acquisition and analysis may provide clinicians with important diagnostic information within minutes. The current article reviews the methodology and application of 3DE for quantitative evaluation of the LV, provides the scientific evidence for its current clinical use, and discusses its current limitations and potential future directions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
How accurately, reproducibly, and efficiently can we measure left ventricular indices using M-mode, 2-dimensional, and 3-dimensional echocardiography in children?Am Heart J. 2008 May;155(5):946-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2007.11.034. Epub 2008 Feb 21. Am Heart J. 2008. PMID: 18440346
-
Automated, machine learning-based, 3D echocardiographic quantification of left ventricular mass.Echocardiography. 2019 Feb;36(2):312-319. doi: 10.1111/echo.14234. Epub 2018 Dec 28. Echocardiography. 2019. PMID: 30592791
-
Evaluation of automated measurement of left ventricular volume by novel real-time 3-dimensional echocardiographic system: Validation with cardiac magnetic resonance imaging and 2-dimensional echocardiography.J Cardiol. 2013 Apr;61(4):281-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2012.11.005. Epub 2013 Mar 5. J Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23466066
-
European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging/Cardiovascular Imaging Department of the Brazilian Society of Cardiology recommendations for the use of cardiac imaging to assess and follow patients after heart transplantation.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015 Sep;16(9):919-48. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jev139. Epub 2015 Jul 2. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015. PMID: 26139361 Review.
-
Three-dimensional echocardiography to assess left ventricular geometry and function.Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2019 Nov;17(11):801-815. doi: 10.1080/14779072.2019.1697234. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2019. PMID: 31770493 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of LV ejection fraction using real-time 3D echocardiography in daily practice: direct comparison of the volumetric and speckle tracking methodologies to CMR.Neth Heart J. 2014 Sep;22(9):383-90. doi: 10.1007/s12471-014-0577-1. Neth Heart J. 2014. PMID: 25143268 Free PMC article.
-
Crown years for noninvasive cardiovascular imaging (part I): 60 years of echocardiography.Neth Heart J. 2013 Apr;21(4):161-2. doi: 10.1007/s12471-013-0381-3. Neth Heart J. 2013. PMID: 23423599 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Role of Automated 3D Echocardiography for Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Assessment.Card Fail Rev. 2017 Nov;3(2):97-101. doi: 10.15420/cfr.2017:14.1. Card Fail Rev. 2017. PMID: 29387460 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of left ventricular volumes and function in anesthetized beagles using real-time three-dimensional echocardiography: 4D-TomTec™ analysis versus 4D-AutLVQ™ analysis in comparison with cardiac magnetic resonance imaging.BMC Vet Res. 2015 Oct 12;11:260. doi: 10.1186/s12917-015-0568-5. BMC Vet Res. 2015. PMID: 26459280 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of right ventriclular systolic function prior to cardiac resynchronization therapy: Does it make any difference?Indian Heart J. 2017 Nov-Dec;69(6):731-735. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2017.05.022. Epub 2017 Jun 3. Indian Heart J. 2017. PMID: 29174250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buck T, Hunold P, Wentz KU, et al. Tomographic three-dimensional echocardiographic determination of chamber size and systolic function in patients with left ventricular aneurysm: comparison to magnetic resonance imaging, cineventriculography, and two-dimensional echocardiography. Circulation. 1997;96:4286–4297. - PubMed
-
- Chuang ML, Hibberd MG, Salton CJ, et al. Importance of imaging method over imaging modality in noninvasive determination of left ventricular volumes and ejection fraction: assessment by two- and three-dimensional echocardiography and magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;35:477–484. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(99)00551-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mannaerts HF, Van Der Heide JA, Kamp O, et al. Quantification of left ventricular volumes and ejection fraction using freehand transthoracic three-dimensional echocardiography: comparison with magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2003;16:101–109. doi: 10.1067/mje.2003.7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kuhl HP, Schreckenberg M, Rulands D, et al. High-resolution transthoracic real-time three-dimensional echocardiography: quantitation of cardiac volumes and function using semi-automatic border detection and comparison with cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43:2083–2090. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2004.01.037. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

