A novel WWTR1-CAMTA1 gene fusion is a consistent abnormality in epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of different anatomic sites
- PMID: 21584898
- PMCID: PMC3264678
- DOI: 10.1002/gcc.20886
A novel WWTR1-CAMTA1 gene fusion is a consistent abnormality in epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of different anatomic sites
Abstract
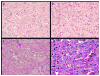
The classification of epithelioid vascular tumors remains challenging, as there is considerable morphological overlap between tumor subtypes, across the spectrum from benign to malignant categories. A t(1;3)(p36.3;q25) translocation was reported in two cases of epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (EHE), however, no follow-up studies have been performed to identify the gene fusion or to assess its prevalence in a larger cohort of patients. We undertook a systematic molecular analysis of 17 EHE, characterized by classic morphological and immunophenotypic features, from various anatomical locations and with different malignant potential. For comparison, we analyzed 13 epithelioid hemangiomas, five epithelioid angiosarcomas, and four epithelioid sarcoma-like EHE. A fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) positional cloning strategy, spanning the cytogenetically defined regions on chromosomes 1p36.3 and 3q25, confirmed rearrangements in two candidate genes from these loci in all EHE cases tested. None of the other benign or malignant epithelioid vascular tumors examined demonstrated these abnormalities. Subsequent reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) confirmed in three EHE the WWTR1-CAMTA1 fusion product. CAMTA1 and WWTR1 have been previously shown to play important roles in oncogenesis. Our results demonstrate the presence of a WWTR1-CAMTA1 fusion in all EHE tested from bone, soft tissue, and visceral location (liver, lung) in keeping with a unique and specific pathological entity. Thus, FISH or RT-PCR analysis for the presence of WWTR1-CAMTA1 fusion may serve as a useful molecular diagnostic tool in challenging diagnoses.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Antonescu CR, Zhang L, Chang NE, Pawel BR, Travis W, Katabi N, Edelman M, Rosenberg AE, Nielsen GP, Dal Cin P, Fletcher CD. EWSR1-POU5F1 fusion in soft tissue myoepithelial tumors. A molecular analysis of sixty-six cases, including soft tissue, bone, and visceral lesions, showing common involvement of the EWSR1 gene. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2010;49:1114–1124. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Attiyeh EF, London WB, Mosse YP, Wang Q, Winter C, Khazi D, McGrady PW, Seeger RC, Look AT, Shimada H, Brodeur GM, Cohn SL, Matthay KK, Maris JM. Chromosome 1p and 11q deletions and outcome in neuroblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2243–2253. - PubMed
-
- Barbashina V, Salazar P, Holland EC, Rosenblum MK, Ladanyi M. Allelic losses at 1p36 and 19q13 in gliomas: correlation with histologic classification, definition of a 150-kb minimal deleted region on 1p36, and evaluation of CAMTA1 as a candidate tumor suppressor gene. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:1119–1128. - PubMed
-
- Bouche N, Scharlat A, Snedden W, Bouchez D, Fromm H. A novel family of calmodulin-binding transcription activators in multicellular organisms. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:21851–21861. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

