hERGAPDbase: a database documenting hERG channel inhibitory potentials and APD-prolongation activities of chemical compounds
- PMID: 21586548
- PMCID: PMC3096323
- DOI: 10.1093/database/bar017
hERGAPDbase: a database documenting hERG channel inhibitory potentials and APD-prolongation activities of chemical compounds
Abstract
Drug-induced QT interval prolongation is one of the most common reasons for the withdrawal of drugs from the market. In the past decade, at least nine drugs, i.e. terfenadine, astemizole, grepafloxacin, terodiline, droperidol, lidoflazine, sertindole, levomethadyl and cisapride, have been removed from the market or their use has been severely restricted because of drug-induced QT interval prolongation. Therefore, this irregularity is a major safety concern in the case of drugs submitted for regulatory approval. The most common mechanism of drug-induced QT interval prolongation may be drug-related inhibition of the human ether-á-go-go-related gene (hERG) channel, which subsequently results in prolongation of the cardiac action potential duration (APD). hERGAPDbase is a database of electrophysiological experimental data documenting potential hERG channel inhibitory actions and the APD-prolongation activities of chemical compounds. All data entries are manually collected from scientific papers and curated by a person. With hERGAPDbase, we aim to provide useful information for chemical and pharmacological scientists and enable easy access to electrophysiological experimental data on chemical compounds. Database URL: http://www.grt.kyushu-u.ac.jp/hergapdbase/.
Figures
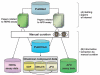


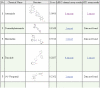

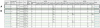
References
-
- Friedrichs GS, Patmore L, Bass A. Non-clinical evaluation of ventricular repolarization (ICH S7B): results of an interim survey of international pharmaceutical companies. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods. 2005;52:6–11. - PubMed
-
- Kang J, Wang L, Chen XL, et al. Interactions of a series of fluoroquinolone antibacterial drugs with the human cardiac K+ channel HERG. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001;59:122–126. - PubMed
-
- Bowlby MR, Peri R, Zhang H, et al. hERG (KCNH2 or Kv11.1) K+ channels: Screening for cardiac arrhythmia risk. Curr. Drug Metab. 2008;9:965–970. - PubMed
-
- Ando K. Drug-induced QT prolongation: individual susceptibility and regulatory issues related to safety pharmacology 2. Evaluation of QT interval prolongation in non-clinical studies according to ICH S7A and S7B and its questions at issue. Jpn. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006;37:201–206.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

