The extracellular regulated kinase-1 (ERK1) controls regulated alpha-secretase-mediated processing, promoter transactivation, and mRNA levels of the cellular prion protein
- PMID: 21586567
- PMCID: PMC3190726
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.208249
The extracellular regulated kinase-1 (ERK1) controls regulated alpha-secretase-mediated processing, promoter transactivation, and mRNA levels of the cellular prion protein
Erratum in
- J Biol Chem. 2011 Sep 23;286(38):33708
- J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 5;288(27):19646
Abstract
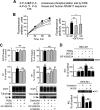
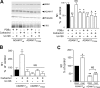
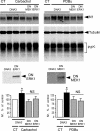
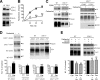
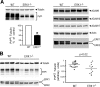
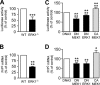
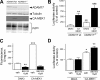
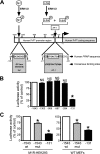
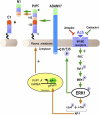
The α-secretases A disintegrin and metalloprotease 10 (ADAM10) and ADAM17 trigger constitutive and regulated processing of the cellular prion protein (PrP(c)) yielding N1 fragment. The latter depends on protein kinase C (PKC)-coupled M1/M3 muscarinic receptor activation and subsequent phosphorylation of ADAM17 on its intracytoplasmic threonine 735. Here we show that regulated PrP(c) processing and ADAM17 phosphorylation and activation are controlled by the extracellular-regulated kinase-1/MAP-ERK kinase (ERK1/MEK) cascade. Thus, reductions of ERK1 or MEK activities by dominant-negative analogs, pharmacological inhibition, or genetic ablation all impair N1 secretion, whereas constitutively active proteins increase N1 recovery in the conditioned medium. Interestingly, we also observed an ERK1-mediated enhanced expression of PrP(c). We demonstrate that the ERK1-associated increase in PrP(c) promoter transactivation and mRNA levels involve transcription factor AP-1 as a downstream effector. Altogether, our data identify ERK1 as an important regulator of PrP(c) cellular homeostasis and indicate that this kinase exerts a dual control of PrP(c) levels through transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms.
Figures
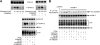

References
-
- Aguzzi A., Calella A. M. (2009) Physiol. Rev. 89, 1105–1152 - PubMed
-
- Linden R., Martins V. R., Prado M. A., Cammarota M., Izquierdo I., Brentani R. R. (2008) Physiol. Rev. 88, 673–728 - PubMed
-
- Chen S. G., Teplow D. B., Parchi P., Teller J. K., Gambetti P., Autilio-Gambetti L. (1995) J. Biol. Chem. 270, 19173–19180 - PubMed
-
- Forloni G., Angeretti N., Chiesa R., Monzani E., Salmona M., Bugiani O., Tagliavini F. (1993) Nature 362, 543–546 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

