Structural basis for immunization with postfusion respiratory syncytial virus fusion F glycoprotein (RSV F) to elicit high neutralizing antibody titers
- PMID: 21586636
- PMCID: PMC3111287
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1106536108
Structural basis for immunization with postfusion respiratory syncytial virus fusion F glycoprotein (RSV F) to elicit high neutralizing antibody titers
Abstract
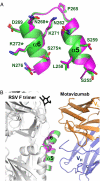
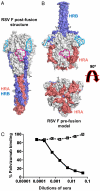
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), the main cause of infant bronchiolitis, remains a major unmet vaccine need despite more than 40 years of vaccine research. Vaccine candidates based on a chief RSV neutralization antigen, the fusion (F) glycoprotein, have foundered due to problems with stability, purity, reproducibility, and potency. Crystal structures of related parainfluenza F glycoproteins have revealed a large conformational change between the prefusion and postfusion states, suggesting that postfusion F antigens might not efficiently elicit neutralizing antibodies. We have generated a homogeneous, stable, and reproducible postfusion RSV F immunogen that elicits high titers of neutralizing antibodies in immunized animals. The 3.2-Å X-ray crystal structure of this substantially complete RSV F reveals important differences from homology-based structural models. Specifically, the RSV F crystal structure demonstrates the exposure of key neutralizing antibody binding sites on the surface of the postfusion RSV F trimer. This unanticipated structural feature explains the engineered RSV F antigen's efficiency as an immunogen. This work illustrates how structural-based antigen design can guide the rational optimization of candidate vaccine antigens.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors are Novartis shareholders and employees of Novartis Vaccines and Diagnostics.
Figures



References
-
- Hall CB. Respiratory syncytial virus. In: Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R, editors. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 7th Ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone; 2010. pp. 2207–2221.
-
- Johnson S, et al. Development of a humanized monoclonal antibody (MEDI-493) with potent in vitro and in vivo activity against respiratory syncytial virus. J Infect Dis. 1997;176:1215–1224. - PubMed
-
- Kim HW, et al. Respiratory syncytial virus disease in infants despite prior administration of antigenic inactivated vaccine. Am J Epidemiol. 1969;89:422–434. - PubMed
-
- Munoz FM, Piedra PA, Glezen WP. Safety and immunogenicity of respiratory syncytial virus purified fusion protein-2 vaccine in pregnant women. Vaccine. 2003;21:3465–3467. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

