Targeting SDF-1/CXCR4 to inhibit tumour vasculature for treatment of glioblastomas
- PMID: 21587260
- PMCID: PMC3111201
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2011.169
Targeting SDF-1/CXCR4 to inhibit tumour vasculature for treatment of glioblastomas
Abstract
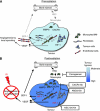
Local recurrence of glioblastomas is a major cause of patient mortality after definitive treatment. This review discusses the roles of the chemokine stromal cell-derived factor-1 and its receptor CXC chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) in affecting the sensitivity of glioblastomas to irradiation. Blocking these molecules prevents or delays tumour recurrence after irradiation by inhibiting the recruitment of CD11b+ monocytes/macrophages that participate in revascularising the tumour. We review the literature pertaining to the mechanism by which revascularisation occurs following tumour irradiation using experimental models. Areas of interest and debate in the literature include the process by which endothelial cells die after irradiation and the identity/origin of the cells that reconstitute the tumour blood vessels after injury. Understanding the processes that mediate tumour revascularisation will guide the improvement of clinical strategies for preventing recurrence of glioblastoma after irradiation.
Figures
References
-
- Aghi M, Cohen KS, Klein RJ, Scadden DT, Chiocca EA (2006) Tumor stromal-derived factor-1 recruits vascular progenitors to mitotic neovasculature, where microenvironment influences their differentiated phenotypes. Cancer Res 66(18): 9054–9064 - PubMed
-
- Aicher A, Rentsch M, Sasaki K, Ellwart JW, Fandrich F, Siebert R, Cooke JP, Dimmeler S, Heeschen C (2007) Nonbone marrow-derived circulating progenitor cells contribute to postnatal neovascularization following tissue ischemia. Circ Res 100(4): 581–589 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

