16-[(E)-Benzyl-idene]-13-hy-droxy-4-methyl-2-phenyl-4,14-diaza-penta-cyclo-[12.3.1.0.0.0]octa-deca-7(12),8,10-triene-6,17-dione
- PMID: 21587787
- PMCID: PMC3006797
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810020271
16-[(E)-Benzyl-idene]-13-hy-droxy-4-methyl-2-phenyl-4,14-diaza-penta-cyclo-[12.3.1.0.0.0]octa-deca-7(12),8,10-triene-6,17-dione
Abstract
In the title compound, C(30)H(26)N(2)O(3), the two pyrrolidine rings adopt twisted and envelope conformations, whereas the cyclo-pentane ring adopts an envelope conformation. The least-squares planes through the pyrrolidine rings form a dihedral angle of 41.72 (10)°. The mol-ecular structure is stabilized by an intra-molecular O-H⋯N hydrogen bond, which generates an S(5) ring motif. Centrosymmetrically related mol-ecules are linked via two pairs of inter-molecular C-H⋯O inter-actions, forming R(2) (2)(16) ring motifs. In the crystal packing, the mol-ecules are linked into two-dimensional networks parallel to the ab plane via C-H⋯O inter-actions.
Figures
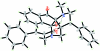

References
-
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
-
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.34, 1555–1573.
-
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Cosier, J. & Glazer, A. M. (1986). J. Appl. Cryst.19, 105–107.
-
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc.97, 1354–1358.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
