3-Acetyl-benzoic acid
- PMID: 21587832
- PMCID: PMC3006848
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810021094
3-Acetyl-benzoic acid
Abstract
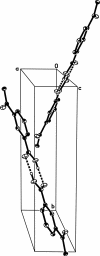
In the crystal structure of the title compound, C(9)H(8)O(3), essentially planar mol-ecules [the carboxyl group makes a dihedral angle of 4.53 (7)° with the plane of the ring, while the acid group forms a dihedral angle of 3.45 (8)° to the ring] aggregate by centrosymmetric hydrogen-bond pairing of ordered carboxyl groups. This yields dimers which have two orientations in a unit cell, creating a herringbone pattern. In addition, two close C-H⋯O inter-molecular contacts exist: one is between a methyl H atom and the ketone of a symmetry-related mol-ecule and the other involves a benzene H atom and the carboxyl group O atom of another mol-ecule. The crystal studied was a non-merohedral twin with twin law [100, 00, 0] and a domain ratio of 0.8104(14): 0.1896(14).
Figures
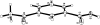
References
-
- Borthwick, P. W. (1980). Acta Cryst. B36, 628–632.
-
- Bruker (2005). SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Bruker (2006). APEX2 Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Cooper, R. I., Gould, R. O., Parsons, S. & Watkin, D. J. (2002). J. Appl. Cryst.35, 168–174.
-
- Dobson, A. J. & Gerkin, R. E. (1996). Acta Cryst. C52, 3078–3081. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
