(Z)-3-(2-{2-[1-(4-Hy-droxy-phen-yl)ethyl-idene]hydrazin-1-yl}-1,3-thia-zol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one
- PMID: 21587863
- PMCID: PMC3006946
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810021604
(Z)-3-(2-{2-[1-(4-Hy-droxy-phen-yl)ethyl-idene]hydrazin-1-yl}-1,3-thia-zol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one
Abstract
In the title compound, C(20)H(15)N(3)O(3)S, an intra-molecular C-H⋯O hydrogen bond generates an S(6) ring motif. The chromene ring system is inclined at dihedral angles of 14.21 (9) and 9.91 (10)°, respectively, with respect to the thia-zole and benzene rings. The thia-zole ring makes a dihedral angle of 24.06 (11)° with the benzene ring. In the crystal structure, O-H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the mol-ecules into a zigzag chain along [20]. Weak N-H⋯O and C-H⋯O inter-actions connect the chains into a three-dimensional network. π-π stacking inter-actions with a centroid-centroid distance of 3.4209 (14) Å are also observed between the chains.
Figures
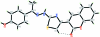
Similar articles
-
3-{2-[2-(2-Fluoro-benzyl-idene)hydrazin-yl]-1,3-thia-zol-4-yl}-2H-chromen-2-one.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2010 May 26;66(Pt 6):o1446-7. doi: 10.1107/S1600536810018647. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2010. PMID: 21579518 Free PMC article.
-
(E)-3-(2-{2-[1-(3-Hy-droxy-phen-yl)ethyl-idene]hydrazin-yl}-1,3-thia-zol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2011 May 1;67(Pt 5):o1072-3. doi: 10.1107/S1600536811012189. Epub 2011 Apr 7. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2011. PMID: 21754396 Free PMC article.
-
3-{2-[2-(3-Hy-droxy-benzyl-idene)hydrazin-1-yl]-1,3-thia-zol-4-yl}-2H-chromen-2-one hemihydrate.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2010 May 29;66(Pt 6):o1498-9. doi: 10.1107/S1600536810019653. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2010. PMID: 21579559 Free PMC article.
-
(E)-6-Bromo-3-{2-[2-(4-chloro-benzyl-idene)hydrazin-yl]thia-zol-5-yl}-2H-chromen-2-one.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2011 Apr 1;67(Pt 4):o1007-8. doi: 10.1107/S1600536811011172. Epub 2011 Mar 31. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2011. PMID: 21754027 Free PMC article.
-
(E)-6-Bromo-3-{2-[2-(2-chloro-benzyl-idene)hydrazin-yl]thia-zol-5-yl}-2H-chromen-2-one dimethyl sulfoxide monosolvate.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2011 Apr 1;67(Pt 4):o1009-10. doi: 10.1107/S1600536811011160. Epub 2011 Mar 31. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2011. PMID: 21754028 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
3-(2-Methyl-amino-1,3-thia-zol-4-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012 Aug 1;68(Pt 8):o2416-7. doi: 10.1107/S1600536812030140. Epub 2012 Jul 10. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012. PMID: 22904868 Free PMC article.
-
Ethyl 2-[(2-oxo-2H-chromen-7-yl)-oxy]acetate.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2013 Mar 6;69(Pt 4):o502. doi: 10.1107/S1600536813005539. Print 2013 Apr 1. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2013. PMID: 23634050 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of (Z)-3-{3-(4-chloro-phen-yl)-2-[(4-chloro-phen-yl)imino]-2,3-di-hydro-thia-zol-4-yl}-2H-chromen-2-one.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2014 Nov 19;70(Pt 12):o1268-9. doi: 10.1107/S1600536814024775. eCollection 2014 Dec 1. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2014. PMID: 25553038 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
-
- Anderson, D. M., Shelley, S., Crick, N. & Buraglio, L. (2002). J. Clin. Pharmacol.42, 1358–1365. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.34, 1555–1573.
-
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
