2-Hy-droxy-5-[(E)-(1H-indol-3-yl-methyl-idene)aza-nium-yl]benzoate
- PMID: 21589591
- PMCID: PMC3011759
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536810048579
2-Hy-droxy-5-[(E)-(1H-indol-3-yl-methyl-idene)aza-nium-yl]benzoate
Abstract
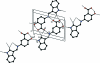
The zwitterionic title compound, C(16)H(12)N(2)O(3), was obtained as a result of the condensation of 5-amino-salicylic acid and 1H-indole-3-carbaldehyde. The whole mol-ecule is roughly planar: the 4-hy-droxy-anilinic group and the 1H-indole-3-carbaldehyde moieties are only slightly twisted, making a dihedral angle of 7.77 (11)°, whereas, the carboxyl-ate group makes a dihedral angle of 3.34 (45)° with the parent 4-hy-droxy-anilinic group. S(6) ring motifs are formed due to intra-molecular O-H⋯O hydrogen bonding. In the crystal, inter-molecular N-H⋯O and C-H⋯O hydrogen bonds build up pseudo-rings with R(1) (2)(4), R(2) (1)(7) and R(2) (2)(14) ring motifs. These pseudo-dimers are further linked by N-H⋯O hydrogen bonds into a chain extending along [101]. C-H⋯π inter-actions also occur, along with offset π-π inter-actions between the anilinic phenyl and the heterocyclic five-membered rings with a centroid-centroid distance of 3.5716 (19) Å.
Figures
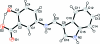
References
-
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.34, 1555–1573.
-
- Bruker (2005). SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Bruker (2009). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Etter, M. C. (1990). Acc. Chem. Res.23, 120–126.
-
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
