Solid self-nanoemulsifying cyclosporin A pellets prepared by fluid-bed coating: preparation, characterization and in vitro redispersibility
- PMID: 21589647
- PMCID: PMC3090276
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S17711
Solid self-nanoemulsifying cyclosporin A pellets prepared by fluid-bed coating: preparation, characterization and in vitro redispersibility
Abstract
Background: The objective of this study was to evaluate fluid-bed coating as a new technique to prepare a pellet-based solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system (SNEDDS) using cyclosporin A as a model of a poorly water-soluble drug.
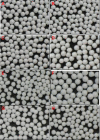
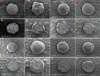
Methods: The rationale of this technique was to entrap a Liquid SNEDDS in the matrix of the coating material, polyvinylpyrrolidone K30, by fluid-bed coating. Pseudoternary phase diagrams were used to screen the liquid SNEDDS formulations. The optimal formulation was composed of Labrafil M(®) 1944 CS, Transcutol P(®), and Cremophor(®) EL in a ratio of 9:14:7. To prepare solid SNEDDS pellets, liquid SNEDDS was first dispersed in an aqueous solution of polyvinylpyrrolidone and then sprayed onto the surface of non-pareil pellets. Upon evaporation of water, polyvinylpyrrolidone precipitated and formed tight films to entrap the liquid SNEDDS. Visual observation and scanning electron microscopic analysis confirmed good appearance of the solid SNEDDS pellets.
Results: Our results indicated that up to 40% of the liquid SNEDDS could be entrapped in the coating layer. Powder x-ray diffraction analysis confirmed nonexistence of crystalline cyclosporin A in the formulation. Solid SNEDDS pellets showed a slower redispersion rate than the liquid SNEDDS. An increase in the total liquid SNEDDS loading led to faster redispersion, whereas increased coating weight (up to 400%) significantly decreased the redispersion rate. Both cyclosporin A loading and protective coating with 5% polyvinylpyrrolidone K30 did not significantly affect the redispersion rate.
Conclusion: It is concluded that fluid-bed coating is a new technique with considerable potential for preparation of pellet-based solid SNEDDS formulations.
Keywords: cyclosporin A; fluid-bed coating; pellets; self-nanoemulsifying; solid.
Figures



References
-
- Lipinski CA. Poor aqueous solubility – an industry wide problem in drug discovery. Am Pharm Rev. 2002;5:82–85.
-
- Dressman J, Reppas C. Drug solubility: How to measure it, how to improve it. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007;59:531–532. - PubMed
-
- Pouton CW, Porter CJH. Formulation of lipid-based delivery systems for oral administration: Materials, methods and strategies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008;60:625–637. - PubMed
-
- Cui J, Yu B, Zhao Y, et al. Enhancement of oral absorption of curcumin by self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems. Int J Pharm. 2009;371:148–155. - PubMed
-
- Woo JS, Song YK, Hong JY. Reduced food-effect and enhanced bioavailability of a self-microemulsifying formulation of itraconazole in healthy volunteers. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2008;33:159–165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

