Liver transplantation in Greek children: 15 years experience
- PMID: 21589827
- PMCID: PMC3094000
- DOI: 10.4081/pr.2010.e14
Liver transplantation in Greek children: 15 years experience
Abstract
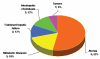
Liver transplantation (LT) is the only available live-saving procedure for children with irreversible liver failure. This paper reports our experience from the follow-up of 16 Greek children with end-stage liver failure who underwent a LT. Over a period of 15 years, 16 pediatric liver recipients received follow up after being subjected to OLT (orthotopic liver transplantation) due to end-stage liver failure. Nine children initially presented with extrahepatic biliary atresia, 2 with acute liver failure after toxic mushroom ingestion, 2 with intrahepatic cholestasis, 2 with metabolic diseases and one with hepatoblastoma. Ten children received a liver transplant in the Organ Transplantation Unit of Aristotle University of Thessaloniki and the rest in other transplant centers. Three transplants came from a living-related donor and 13 from a deceased donor. Six children underwent immunosuppressive treatment with cyclosporine, mycophenolate mofetil and corticosteroids, and 7 with tacrolimus, mycophenolate mofetil and corticosteroids. Three out of 16 children died within the first month after the transplantation due to post-transplant complications. Three children presented with acute rejection and one with chronic organ rejection which was successfully managed. Five children presented with cytomegalovirus infection, 5 with Epstein-Barr virus, 2 with HSV(1,2), 2 with ParvoB19 virus, 2 with varicella-zoster virus and one with C. Albicans infection. One child presented with upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage and one with small biliary paucity. A satisfying outcome was achieved in most cases, with good graft function, except for the patient with small biliary paucity who required re-transplantation.The long-term clinical course of liver transplanted children is good under the condition that they are attended in specialized centers.
Keywords: Greek children.; liver transplantation.
Figures
References
-
- Starzl TE. History of Liver and Other Splanchnic Organ Transplantation. In: Busutill RW, Klintmalm GB, editors. Transplantation of the Liver. Philadelphia, Pa: W.B. Saunders; 1996. pp. 3–22.
-
- Otte JB. History of pediatric liver transplantation. Where are we coming from? Where do we stand? Pediatr Transplant. 2002;6:378–87. - PubMed
-
- Alagille D. History of pediatric liver transplantation in Europe. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2004;67:172–5. - PubMed
-
- Schafer DF. Liver transplantation. Looking back, looking forward. In: Maddrey WC, Schiff ER, Sorrell MF, editors. Transplantation of the Liver. Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott, Williams, & Wilkins; 2001.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources