Small worlds and semantic network growth in typical and late talkers
- PMID: 21589924
- PMCID: PMC3092758
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019348
Small worlds and semantic network growth in typical and late talkers
Abstract
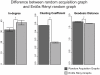
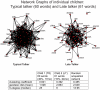
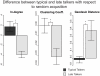
Network analysis has demonstrated that systems ranging from social networks to electric power grids often involve a small world structure-with local clustering but global ac cess. Critically, small world structure has also been shown to characterize adult human semantic networks. Moreover, the connectivity pattern of these mature networks is consistent with lexical growth processes in which children add new words to their vocabulary based on the structure of the language-learning environment. However, thus far, there is no direct evidence that a child's individual semantic network structure is associated with their early language learning. Here we show that, while typically developing children's early networks show small world structure as early as 15 months and with as few as 55 words, children with language delay (late talkers) have this structure to a smaller degree. This implicates a maladaptive bias in word acquisition for late talkers, potentially indicating a preference for "oddball" words. The findings provide the first evidence of a link between small-world connectivity and lexical development in individual children.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Newman MEJ. The structure and function of complex networks. SIAM Review. 2003;45:167–256.
-
- Davis GF, Gardner BB, Gardner MR. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 1941. Deep South.
-
- Seglen P O. The skewness of science. Journal of American Society for Information Science. 1992;43:628–638.
-
- Sporns O. Network analysis, complexity and brain function. Complexity. 2002;8:56–60.
-
- Borge-Holthoefer J, Arenas A. Semantic networks: Structure and dynamics. Entropy. 2010;12:1264–1302.

