Association of PPP2CA polymorphisms with systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility in multiple ethnic groups
- PMID: 21590681
- PMCID: PMC3163110
- DOI: 10.1002/art.30452
Association of PPP2CA polymorphisms with systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility in multiple ethnic groups
Erratum in
- Arthritis Rheum. 2011 Nov;63(11):3521. Alarcón, Graciela S [added]
Abstract
Objective: T cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) express increased amounts of PP2Ac, which contributes to decreased production of interleukin-2 (IL-2). Because IL-2 is important in the regulation of several aspects of the immune response, it has been proposed that PP2Ac contributes to the expression of SLE. This study was designed to determine whether genetic variants of PPP2AC are linked to the expression of SLE and specific clinical manifestations and account for the increased expression of PP2Ac.
Methods: We conducted a trans-ethnic study of 8,695 SLE cases and 7,308 controls of 4 different ancestries. Eighteen single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) across PPP2CA were genotyped using an Illumina custom array. PPP2CA expression in SLE and control T cells was analyzed by real-time polymerase chain reaction.
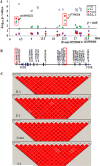
Results: A 32-kb haplotype comprising multiple SNPs of PPP2CA showed significant association with SLE in Hispanic Americans, European Americans, and Asians, but not in African Americans. Conditional analyses revealed that SNP rs7704116 in intron 1 showed consistently strong association with SLE across Asian, European American, and Hispanic American populations (odds ratio 1.3 [95% confidence interval 1.14-1.31], meta-analysis P=3.8×10(-7)). In European Americans, the largest ethnic data set studied, the risk A allele of rs7704116 was associated with the presence of renal disease, anti-double-stranded DNA, and anti-RNP antibodies. PPP2CA expression was ∼2-fold higher in SLE patients carrying the rs7704116 AG genotype than those carrying the GG genotype (P=0.007).
Conclusion: Our data provide the first evidence of an association between PPP2CA polymorphisms and elevated PP2Ac transcript levels in T cells, which implicates a new molecular pathway for SLE susceptibility in European Americans, Hispanic Americans, and Asians.
Copyright © 2011 by the American College of Rheumatology.
Figures

References
-
- Eichhorn PJ, Creyghton MP, Bernards R. Protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunits and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1795(1):1–15. - PubMed
-
- Purev E, Giordano A, Soprano DR, Soprano KJ. Interaction of PP2A catalytic subunit with Rb2/p130 is required for all-trans retinoic acid suppression of ovarian carcinoma cell growth. J Cell Physiol. 2006;206(2):495–502. - PubMed
-
- Shi Y. Serine/threonine phosphatases: mechanism through structure. Cell. 2009;139(3):468–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000154/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI-068787/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01-AR-49084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI-063274/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-025741/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AR-053483/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01-AI-083194/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR053308/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI063274/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R37-AI-024717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM103510/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60-AR-049459/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR020143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24-AR-002138/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-025005/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR-043814/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR-042460/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 17761/ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01-AR-043274/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AR-62277/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024999/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR053483/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI083790/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA-141700/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR015577/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01-AI-50026/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P60-AR-053308/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-024999/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 RR031152/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR-029882/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025741/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- I-ULI-RR-025014-02/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P20-RR-020143/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K08-AI-083790/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AR062277/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 AR058621/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI068787/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043814/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR049459/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI024717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR042460/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR033062/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-00079/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025014/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029882/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- L30 AI071651/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR-051545-01A2/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043727/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA141700/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR-33062/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI078004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AR002138/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P20-RR-015577/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- LRP-AI-071651/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P602-AR-30692/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI083194/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AR-43727/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI070304/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AR030692/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC1-AR-058621/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AR049084/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR051545/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR043274/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21-AI-070304/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI050026/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

