Volumetric bone mineral density and bone structure in childhood chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 21590737
- PMCID: PMC3304436
- DOI: 10.1002/jbmr.427
Volumetric bone mineral density and bone structure in childhood chronic kidney disease
Abstract
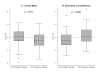
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is associated with increased fracture risk and skeletal deformities. The impact of CKD on volumetric bone mineral density (vBMD) and cortical dimensions during growth is unknown. Tibia quantitative computed tomographic scans were obtained in 156 children with CKD [69 stages 2 to 3, 51 stages 4 to 5, and 36 stage 5D (dialysis)] and 831 healthy participants aged 5 to 21 years. Sex-, race-, and age- or tibia length-specific Z-scores were generated for trabecular BMD (TrabBMD), cortical BMD (CortBMD), cortical area (CortArea) and endosteal circumference (EndoC). Greater CKD severity was associated with a higher TrabBMD Z-score in younger participants (p < .001) compared with healthy children; this association was attenuated in older participants (interaction p < .001). Mean CortArea Z-score was lower (p < .01) in CKD 4-5 [-0.49, 95% confidence interval (CI) -0.80, -0.18)] and CKD 5D (-0.49, 95% CI -0.83, -0.15) compared with healthy children. Among CKD participants, parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels were positively associated with TrabBMD Z-score (p < .01), and this association was significantly attenuated in older participants (interaction p < .05). Higher levels of PTH and biomarkers of bone formation (bone-specific alkaline phosphatase) and resorption (serum C-terminal telopeptide of type 1 collagen) were associated with lower CortBMD and CortArea Z-scores and greater EndoC Z-score (r = 0.18-0.36, all p ≤ .02). CortBMD Z-score was significantly lower in CKD participants with PTH levels above versus below the upper limit of the Kidney Disease Outcome Quality Initiative (KDOQI) CKD stage-specific target range: -0.46 ± 1.29 versus 0.12 ± 1.14 (p < .01). In summary, childhood CKD and secondary hyperparathyroidism were associated with significant reductions in cortical area and CortBMD and greater TrabBMD in younger children. Future studies are needed to establish the fracture implications of these alterations and to determine if cortical and trabecular abnormalities are reversible.
Copyright © 2011 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors state that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Gilsanz V, Skaggs DL, Kovanlikaya A, Sayre J, Loro ML, Kaufman F, Korenman SG. Differential effect of race on the axial and appendicular skeletons of children. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998;83(5):1420–7. - PubMed
-
- Alem AM, Sherrard DJ, Gillen DL, Weiss NS, Beresford SA, Heckbert SR, Wong C, Stehman-Breen C. Increased risk of hip fracture among patients with end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2000;58(1):396–9. - PubMed
-
- Ball AM, Gillen DL, Sherrard D, Weiss NS, Emerson SS, Seliger SL, Kestenbaum BR, Stehman-Breen C. Risk of hip fracture among dialysis and renal transplant recipients. Jama. 2002;288(23):3014–8. - PubMed
-
- Nickolas TL, McMahon DJ, Shane E. Relationship between moderate to severe kidney disease and hip fracture in the United States. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17(11):3223–32. - PubMed

