Novel 16-channel receive coil array for accelerated upper airway MRI at 3 Tesla
- PMID: 21590804
- PMCID: PMC3135687
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.22742
Novel 16-channel receive coil array for accelerated upper airway MRI at 3 Tesla
Abstract
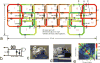
Upper airway MRI can provide a noninvasive assessment of speech and swallowing disorders and sleep apnea. Recent work has demonstrated the value of high-resolution three-dimensional imaging and dynamic two-dimensional imaging and the importance of further improvements in spatio-temporal resolution. The purpose of the study was to describe a novel 16-channel 3 Tesla receive coil that is highly sensitive to the human upper airway and investigate the performance of accelerated upper airway MRI with the coil. In three-dimensional imaging of the upper airway during static posture, 6-fold acceleration is demonstrated using parallel imaging, potentially leading to capturing a whole three-dimensional vocal tract with 1.25 mm isotropic resolution within 9 sec of sustained sound production. Midsagittal spiral parallel imaging of vocal tract dynamics during natural speech production is demonstrated with 2 × 2 mm(2) in-plane spatial and 84 ms temporal resolution.
Copyright © 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Shellock FG, Schatz CJ, Julien P, Steinberg F, Foo TK, Hopp ML, Westbrook PR. Occlusion and narrowing of the pharyngeal airway in obstructive sleep apnea: evaluation by ultrafast spoiled GRASS MR imaging. Am J Roentgenology. 1992;158:1019–1024. - PubMed
-
- Arens R, McDonough JM, Costarino AT, Mahboubi S, Tayag-Kier CE, Maislin G, Schwab RJ, Pack AI. Magnetic resonance imaging of the upper airway structure of children with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;164:698–703. - PubMed
-
- Hartl DM, Albiter M, Kolb F, Luboinski B, Sigal R. Morphologic parameters of normal swallowing events using single-shot fast spin echo dynamic MRI. Dysphagia. 2003;18:255–262. - PubMed
-
- Narayanan SS, Alwan AA, Haker K. An articulatory study of fricative consonants using magnetic resonance imaging. J Acoust Soc Am. 1995;98(3):1325–1347.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

