Bioelectronic delivery of electrons to cytochrome P450 enzymes
- PMID: 21591685
- PMCID: PMC3128182
- DOI: 10.1021/jp201235m
Bioelectronic delivery of electrons to cytochrome P450 enzymes
Abstract
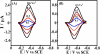
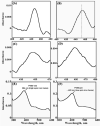
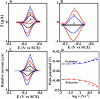
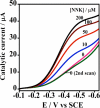
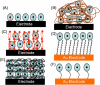
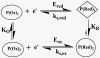
Cytochrome P450s (cyt P450s) are the major oxidative enzymes in human oxidative metabolism of drugs and xenobiotic chemicals. In nature, the iron heme cyt P450s utilize oxygen and electrons delivered from NADPH by a reductase enzyme to oxidize substrates stereo- and regioselectively. Significant research has been directed toward achieving these events electrochemically. This Feature Article discusses the direct electrochemistry of cyt P450s in thin films and the utilization of such films for electrochemically driven biocatalysis. Maintaining and confirming structural integrity and catalytic activity of cyt P450s in films is an essential feature of these efforts. We highlight here our efforts to elucidate the influence of iron heme spin state and secondary structure of human cyt P450s on voltammetric and biocatalytic properties, using methodologies to quantitatively describe the dynamics of these processes in thin films. We also describe the first cyt P450/reductase films that accurately mimic the natural biocatalytic pathway and show how they can be used with voltammetry to elucidate key mechanistic features. Such bioelectronic cyt P450 systems have high value for future drug development, toxicity screening, fundamental investigations, and chemical synthesis systems.
Figures







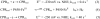
References
-
- Schenkman JB, Greim H, editors. Cytochrome P450. Springer-Verlag; Berlin: 1993.
-
- Ortiz de Montellano PR, editor. Cytochrome P450. Kluwer/Plenum; New York: 2005.
-
- Kramer JA, Sagartz JE, Morris DL. Nature Rev. Drug Discov. 2007;6:636–649. - PubMed
-
- Sansen S, Yano JK, Reynald RL, Schoch GA, Griffin KJ, Stout CD, Johnson EF. J. Biol. Chem. 2007;282:14348–14355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

