Integrin βν-mediated phagocytosis of apoptotic cells in Drosophila embryos
- PMID: 21592968
- PMCID: PMC3138285
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.204503
Integrin βν-mediated phagocytosis of apoptotic cells in Drosophila embryos
Abstract
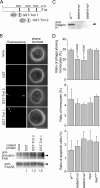
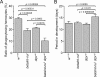
To identify molecules that play roles in the clearance of apoptotic cells by Drosophila phagocytes, we examined a series of monoclonal antibodies raised against larval hemocytes for effects on phagocytosis in vitro. One antibody that inhibited phagocytosis recognized terribly reduced optic lobes (Trol), a core protein of the perlecan-type proteoglycan, and the level of phagocytosis in embryos of a Trol-lacking fly line was lower than in a control line. The treatment of a hemocyte cell line with a recombinant Trol protein containing the amino acid sequence RGD augmented the phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase, a hallmark of integrin activation. A loss of integrin βν, one of the two β subunits of Drosophila integrin, brought about a reduction in the level of apoptotic cell clearance in embryos. The presence of integrin βν at the surface of embryonic hemocytes was confirmed, and forced expression of integrin βν in hemocytes of an integrin βν-lacking fly line recovered the defective phenotype of phagocytosis. Finally, the level of phagocytosis in a fly line that lacks both integrin βν and Draper, another receptor required for the phagocytosis of apoptotic cells, was lower than that in a fly line lacking either protein. We suggest that integrin βν serves as a phagocytosis receptor responsible for the clearance of apoptotic cells in Drosophila, independent of Draper.
Figures

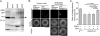
References
-
- Savill J., Fadok V. (2000) Nature 407, 784–788 - PubMed
-
- Liao D. J. (2005) Med. Hypotheses 65, 23–28 - PubMed
-
- Nakanishi Y., Nagaosa K., Shiratsuchi A. (2011) Dev. Growth Differ. 53, 149–160 - PubMed
-
- Lauber K., Blumenthal S. G., Waibel M., Wesselborg S. (2004) Mol. Cell 14, 277–287 - PubMed
-
- Ravichandran K. S., Lorenz U. (2007) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 7, 964–974 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

