Alzheimer's disease brain-derived amyloid-β-mediated inhibition of LTP in vivo is prevented by immunotargeting cellular prion protein
- PMID: 21593310
- PMCID: PMC6622598
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6500-10.2011
Alzheimer's disease brain-derived amyloid-β-mediated inhibition of LTP in vivo is prevented by immunotargeting cellular prion protein
Abstract
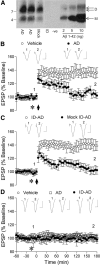
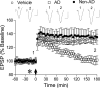
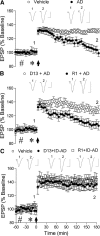
Synthetic amyloid-β protein (Aβ) oligomers bind with high affinity to cellular prion protein (PrP(C)), but the role of this interaction in mediating the disruption of synaptic plasticity by such soluble Aβ in vitro is controversial. Here we report that intracerebroventricular injection of Aβ-containing aqueous extracts of Alzheimer's disease (AD) brain robustly inhibits long-term potentiation (LTP) without significantly affecting baseline excitatory synaptic transmission in the rat hippocampus in vivo. Moreover, the disruption of LTP was abrogated by immunodepletion of Aβ. Importantly, intracerebroventricular administration of antigen-binding antibody fragment D13, directed to a putative Aβ-binding site on PrP(C), prevented the inhibition of LTP by AD brain-derived Aβ. In contrast, R1, a Fab directed to the C terminus of PrP(C), a region not implicated in binding of Aβ, did not significantly affect the Aβ-mediated inhibition of LTP. These data support the pathophysiological significance of SDS-stable Aβ dimer and the role of PrP(C) in mediating synaptic plasticity disruption by soluble Aβ.
Figures
References
-
- Balducci C, Beeg M, Stravalaci M, Bastone A, Sclip A, Biasini E, Tapella L, Colombo L, Manzoni C, Borsello T, Chiesa R, Gobbi M, Salmona M, Forloni G. Synthetic amyloid-beta oligomers impair long-term memory independently of cellular prion protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:2295–2300. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bi X, Gall CM, Zhou J, Lynch G. Uptake and pathogenic effects of amyloid beta peptide 1-42 are enhanced by integrin antagonists and blocked by NMDA receptor antagonists. Neuroscience. 2002;112:827–840. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
