Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 facilitates neuronal glutathione synthesis by upregulating neuronal excitatory amino acid transporter 3 expression
- PMID: 21593323
- PMCID: PMC3339848
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6577-10.2011
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 facilitates neuronal glutathione synthesis by upregulating neuronal excitatory amino acid transporter 3 expression
Abstract
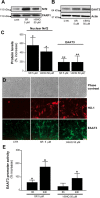
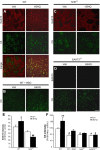
Astrocytes support neuronal antioxidant capacity by releasing glutathione, which is cleaved to cysteine in brain extracellular space. Free cysteine is then taken up by neurons through excitatory amino acid transporter 3 [EAAT3; also termed Slc1a1 (solute carrier family 1 member 1)] to support de novo glutathione synthesis. Activation of the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)-antioxidant responsive element (ARE) pathway by oxidative stress promotes astrocyte release of glutathione, but it remains unknown how this release is coupled to neuronal glutathione synthesis. Here we evaluated transcriptional regulation of the neuronal cysteine transporter EAAT3 by the Nrf2-ARE pathway. Nrf2 activators and Nrf2 overexpression both produced EAAT3 transcriptional activation in C6 cells. A conserved ARE-related sequence was found in the EAAT3 promoter of several mammalian species. This ARE-related sequence was bound by Nrf2 in mouse neurons in vivo as observed by chromatin immunoprecipitation. Chemical activation of the Nrf2-ARE pathway in mouse brain increased both neuronal EAAT3 levels and neuronal glutathione content, and these effects were abrogated in mice genetically deficient in either Nrf2 or EAAT3. Selective overexpression of Nrf2 in brain neurons by lentiviral gene transfer was sufficient to upregulate both neuronal EAAT3 protein and glutathione content. These findings identify a mechanism whereby Nrf2 activation can coordinate astrocyte glutathione release with neuronal glutathione synthesis through transcriptional upregulation of neuronal EAAT3 expression.
Figures






References
-
- Alam J, Stewart D, Touchard C, Boinapally S, Choi AM, Cook JL. Nrf2, a Cap‘n’Collar transcription factor, regulates induction of the heme oxygenase-1 gene. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:26071–26078. - PubMed
-
- Aoyama K, Suh SW, Hamby AM, Liu J, Chan WY, Chen Y, Swanson RA. Neuronal glutathione deficiency and age-dependent neurodegeneration in the EAAC1 deficient mouse. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:119–126. - PubMed
-
- Aoyama K, Matsumura N, Watabe M, Nakaki T. Oxidative stress on EAAC1 is involved in MPTP-induced glutathione depletion and motor dysfunction. Eur J Neurosci. 2008a;27:20–30. - PubMed
-
- Aoyama K, Watabe M, Nakaki T. Regulation of neuronal glutathione synthesis. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008b;108:227–238. - PubMed
-
- Bianchi MG, Gazzola GC, Cagnin S, Kagechika H, Bussolati O. The ATRA-dependent overexpression of the glutamate transporter EAAC1 requires RARbeta induction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1788:1861–1868. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
