Holotranscobalamin, a marker of vitamin B-12 status: analytical aspects and clinical utility
- PMID: 21593496
- PMCID: PMC3127504
- DOI: 10.3945/ajcn.111.013458
Holotranscobalamin, a marker of vitamin B-12 status: analytical aspects and clinical utility
Abstract
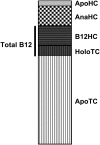
Approximately one-quarter of circulating cobalamin (vitamin B-12) binds to transcobalamin (holoTC) and is thereby available for the cells of the body. For this reason, holoTC is also referred to as active vitamin B-12. HoloTC was suggested as an optimal marker of early vitamin B-12 deficiency >20 y ago. This suggestion led to the development of suitable assays for measurement of the compound and clinical studies that aimed to show the benefit of measurement of holoTC rather than of vitamin B-12. Today holoTC can be analyzed by 3 methods: direct measurement of the complex between transcobalamin and vitamin B-12, measurement of vitamin B-12 attached to transcobalamin, or measurement of the amount of transcobalamin saturated with vitamin B-12. These 3 methods give similar results, but direct measurement of holoTC complex is preferable in the clinical setting from a practical point of view. HoloTC measurement has proven useful for the identification of the few patients who suffer from transcobalamin deficiency. In addition, holoTC is part of the CobaSorb test and therefore useful for assessment of vitamin B-12 absorption. Clinical studies that compare the ability of holoTC and vitamin B-12 to identify individuals with vitamin B-12 deficiency (elevated concentration of methylmalonic acid) suggest that holoTC performs better than total vitamin B-12. To date, holoTC has not been used for population-based assessments of vitamin B-12 status, but we suggest that holoTC is a better marker than total vitamin B-12 for such studies.
Figures
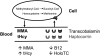

References
-
- Herzlich B, Herbert V. Depletion of serum holotranscobalamin II. An early sign of negative vitamin B12 balance. Lab Invest 1988;58:332–7 - PubMed
-
- Nexo E, Andersen J. Unsaturated and cobalamin saturated transcobalamin I and II in normal human plasma. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 1977;37:723–8 - PubMed
-
- Hom BL, Olesen HA. Plasma clearance of 57cobalt-labelled vitamin B12 bound in vitro and in vivo to transcobalamin I and II. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 1969;23:201–11 - PubMed
-
- Nexo E, Gimsing P. Turnover in humans of iodine- and cobalamin-labeled transcobalamin I and of iodine-labeled albumin. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 1975;35:391–8 - PubMed
-
- Kolhouse JF, Kondo H, Allen NC, Podell E, Allen RH. Cobalamin analogues are present in human plasma and can mask cobalamin deficiency because current radioisotope dilution assays are not specific for true cobalamin. N Engl J Med 1978;299:785–92 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

