Cancer to bone: a fatal attraction
- PMID: 21593787
- PMCID: PMC3666847
- DOI: 10.1038/nrc3055
Cancer to bone: a fatal attraction
Abstract
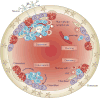
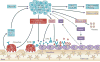
When cancer metastasizes to bone, considerable pain and deregulated bone remodelling occurs, greatly diminishing the possibility of cure. Metastasizing tumour cells mobilize and sculpt the bone microenvironment to enhance tumour growth and to promote bone invasion. Understanding the crucial components of the bone microenvironment that influence tumour localization, along with the tumour-derived factors that modulate cellular and protein matrix components of bone to favour tumour expansion and invasion, is central to the pathophysiology of bone metastases. Basic findings of tumour-bone interactions have uncovered numerous therapeutic opportunities that focus on the bone microenvironment to prevent and treat bone metastases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare
Figures




References
-
- Roodman GD. Mechanisms of bone metastasis. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1655–1664. - PubMed
-
- Coleman RE. Metastatic bone disease: clinical features, pathophysiology and treatment strategies. Cancer Treat Rev. 2001;27:165–176. - PubMed
-
- Mundy GR. Metastasis to bone: causes, consequences and therapeutic opportunities. Nature Rev Cancer. 2002;2:584–593. - PubMed
-
- Fukutomi M, et al. Increased incidence of bone metastases in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001;13:1083–1088. - PubMed
-
- Guise TA, et al. Basic mechanisms responsible for osteolytic and osteoblastic bone metastases. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:6213s–6216s. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01- DK53904/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA143057/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK067333/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK065837/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01‑CA52152/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA069568/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK053904/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA69158/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA069158/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK053904/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK065837/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK067333/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01‑CA093900/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01‑CA100730/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA097250/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA143057/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA100730/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA093900/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

