Lessons on the pathogenesis of aneurysm from heritable conditions
- PMID: 21593863
- PMCID: PMC3622871
- DOI: 10.1038/nature10145
Lessons on the pathogenesis of aneurysm from heritable conditions
Abstract
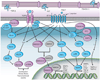
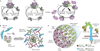
Aortic aneurysm is common, accounting for 1-2% of all deaths in industrialized countries. Early theories of the causes of human aneurysm mostly focused on inherited or acquired defects in components of the extracellular matrix in the aorta. Although several mutations in the genes encoding extracellular matrix proteins have been recognized, more recent discoveries have shown important perturbations in cytokine signalling cascades and intracellular components of the smooth muscle contractile apparatus. The modelling of single-gene heritable aneurysm disorders in mice has shown unexpected involvement of the transforming growth factor-β cytokine pathway in aortic aneurysm, highlighting the potential for new therapeutic strategies.
Figures

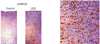
References
-
- Loeys B, et al. Homozygosity for a missense mutation in fibulin-5 (FBLN5) results in a severe form of cutis laxa. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2002;11:2113–2118. - PubMed
-
- Dasouki M, et al. Compound heterozygous mutations in fibulin-4 causing neonatal lethal pulmonary artery occlusion, aortic aneurysm, arachnodactyly, and mild cutis laxa. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2007;143A:2635–2641. - PubMed
-
- Bergen AA, et al. Mutations in ABCC6 cause pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Nature Genet. 2000;25:228–231. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

