Molecular bases of genetic diversity and evolution of the immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (IGHV) gene locus in leporids
- PMID: 21594770
- PMCID: PMC3404511
- DOI: 10.1007/s00251-011-0533-9
Molecular bases of genetic diversity and evolution of the immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (IGHV) gene locus in leporids
Abstract
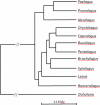
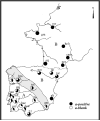
The rabbit has long been a model for studies of the immune system. Work using rabbits contributed both to the battle against infectious diseases such as rabies and syphilis, and to our knowledge, of antibodies' structure, function, and regulated expression. With the description of rabbit Ig allotypes, the discovery of different gene segments encoding immunoglobulins became possible. This challenged the "one gene-one protein" dogma. The observation that rabbit allotypic specificities of the variable regions were present on IgM and IgG molecules also led to the hypothesis of Ig class switching. Rabbit allotypes contributed to the documentation of phenomena such as allelic exclusion and imbalance in production of allelic gene products. During the last 30 years, the rabbit Ig allotypes revealed a number of unique features, setting them apart from mice, humans, and other mammals. Here, we review the most relevant findings concerning the rabbit IGHV. Among these are the preferential usage of one VH gene in VDJ rearrangements, the existence of trans-species polymorphism in the IGHV locus revealed by serology and confirmed by sequencing IGHV genes in Lepus, the unusually large genetic distances between allelic lineages and the fact that the antibody repertoire is diversified in this species only after birth. The whole genome sequence of a rabbit, plus re-sequencing of additional strains and related genera, will allow further evolutionary investigations of antibody variation. Continued research will help define the roles that genetic, allelic, and population diversity at antibody loci may play in host-parasite interactions.
Figures
References
-
- Allegrucci M, Newman BA, Young-Cooper GO, Alexander CB, Meier D, Kelus AS, Mage RG. Altered phenotypic expression of immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable-region (VH) genes in Alicia rabbits probably reflects a small deletion in the VH genes closest to the joining region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990;87(14):5444–5448. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alves PC, Hackländer K. Lagomorph species: Geographical distribution and conservation status. In: Alves PC, Ferrand N, Hackländer K, editors. Lagomorph Biology. Springer; Berlin Heidelberg: 2008. pp. 395–405.
-
- Becker RS, Knight KL. Somatic diversification of immunoglobulin heavy chain VDJ genes: evidence for somatic gene conversion in rabbits. Cell. 1990;63(5):987–997. - PubMed
-
- Biju-Duval C, Ennafaa H, Dennebouy N, Monnerot M, Mignotte F, Soriguer RC, Gaaïed AE, Hili AE, Mounolou J-C. Mitochondrial DNA evolution in lagomorphs: Origin of systematic heteroplasmy and organization of diversity in European rabbits. Journal of Molecular Evolution. 1991;33(1):92–102.
-
- Bouton C, van der Loo W. The trans-species nature of rabbit b locus polymorphism is supported by studies on the snow-shoe hare. Immunogenetics. 1997;45(6):444–446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

