Premature aging-related peripheral neuropathy in a mouse model of progeria
- PMID: 21596054
- PMCID: PMC3179831
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mad.2011.04.010
Premature aging-related peripheral neuropathy in a mouse model of progeria
Abstract
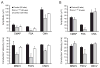
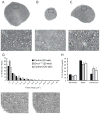
Peripheral neuropathy is a common aging-related degenerative disorder that interferes with daily activities and leads to increased risk of falls and injury in the elderly. The etiology of most aging-related peripheral neuropathy is unknown. Inherited defects in several genome maintenance mechanisms cause tissue-specific accelerated aging, including neurodegeneration. We tested the hypothesis that a murine model of XFE progeroid syndrome, caused by reduced expression of ERCC1-XPF DNA repair endonuclease, develops peripheral neuropathy. Nerve conduction studies revealed normal nerve function in young adult (8 week) Ercc1(-/Δ) mice, but significant abnormalities in 20 week-old animals. Morphologic and ultrastructural analysis of the sciatic nerve from mutant mice revealed significant alterations at 20 but not 8 weeks of age. We conclude that Ercc1(-/Δ) mice have accelerated spontaneous peripheral neurodegeneration that mimics aging-related disease. This provides strong evidence that DNA damage can drive peripheral neuropathy and offers a rapid and novel model to test therapies.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Abbas A, Yang G, Fakih M. Management of anal cancer in 2010. Part 2: current treatment standards and future directions. Oncology (Williston Park) 24:417–24. - PubMed
-
- Authier N, Gillet JP, Fialip J, Eschalier A, Coudore F. An animal model of nociceptive peripheral neuropathy following repeated cisplatin injections. Exp Neurol. 2003;182:12–20. - PubMed
-
- Bouche P, Cattelin F, Saint-Jean O, Leger JM, Queslati S, Guez D, Moulonguet A, Brault Y, Aquino JP, Simunek P. Clinical and electrophysiological study of the peripheral nervous system in the elderly. J Neurol. 1993;240:263–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA119298/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079307/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA076541/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA119298/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30AG024827/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AR051456/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG033907/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG024827/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- DK04493/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG024827/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK079307/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ES016114/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS058451/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- CA076541/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AG033907/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS058451/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK044935/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES016114/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

