Glutathione preconditioning ameliorates mitochondria dysfunction during warm pulmonary ischemia-reperfusion injury
- PMID: 21596579
- PMCID: PMC3241131
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2011.02.081
Glutathione preconditioning ameliorates mitochondria dysfunction during warm pulmonary ischemia-reperfusion injury
Abstract
Objectives: Reduced glutathione (GSH) has been shown to improve pulmonary graft preservation. Mitochondrial dysfunction is regarded to be the motor of ischemia-reperfusion injury (IR) in solid organs. We have shown previously that IR induces pulmonary mitochondrial damage. This study elucidates the impact of GSH preconditioning on the integrity and function of pulmonary mitochondria in the setting of warm pulmonary IR.
Methods: Wistar rats were subjected to control, sham, and to two-study-group conditions (IR30/60 and GSH-IR30/60) receiving IR with or without GSH preconditioning. Rats were anesthetized and received mechanical ventilation. Pulmonary in situ clamping followed by reperfusion generated IR. Mitochondria were isolated from pulmonary tissue. Respiratory chain complexes activities (I-IV) were analyzed by polarography. Mitochondrial viability (Ca2+-induced swelling) and membrane integrity (citrate synthase assay) were determined. Subcellular-fractional cytochrome C-content (Cyt C) was quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) was analyzed by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) after energizing and uncoupling. Inflammatory activation was determined by myeloperoxidase activity (MPO), matrix-metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) activity by gel zymography.
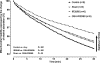
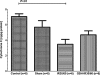
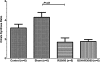
Results: Pulmonary IR significantly reduced mitochondrial viability in combination with ΔΨm hyper-polarization. GSH preconditioning improved mitochondrial viability and normalized ΔΨm. Cyt C was reduced after IR; GSH protected from Cyt C liberation. Respiratory chain complex activities (I, II, III) declined during IR; GSH protected complex II function. GSH also protected from MMP-9 and neutrophil sequestration (P>.05).
Conclusions: GSH preconditioning is effective to prevent mitochondrial death and improves complex II function during IR, but not mitochondrial membrane stability. GSH-mediated amelioration of ΔΨm hyper-polarization appears to be the key factor of mitochondrial protection.
Figures



References
-
- Christie JD, Edwards LB, Aurora P, Dobbels F, Kirk R, Rahmel AO, Stehlik J, Taylor DO, Kucheryavaya AY, Hertz MI. The registry of the international society for heart and lung transplantation: twenty-sixth official adult lung and heart-lung transplantation report-2009. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2009;28:1031–49. - PubMed
-
- J Heart Lung Transplant. 2011;30:811–8. Sommer SP, Sommer S, Sinha B, Wiedemann J, Otto C, Aleksic I, Schimmer C, Leyh RG. Ischemia-reperfusion injury-induced pulmonary mitochondrial damage. - PubMed
-
- Sommer SP, Warnecke G, Hohlfeld JM, Gohrbandt B, Niedermeyer J, Kofidis T, Haverich A, Struber M. Pulmonary preservation with LPD and celsior solution in porcine lung transplantation after 24 h of cold ischemia. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2004;26:151–7. - PubMed
-
- Sommer SP, Gohrbandt B, Fischer S, Hohlfeld JM, Warnecke G, Avsar M, Struber M. Glutathione improves the function of porcine pulmonary grafts stored for twenty-four hours in low-potassium dextran solution. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;130:864–9. - PubMed
-
- Bugger H, Chemnitius J-M., Doenst T. Differential changes in respiratory capacity and ischemia tolerance of isolated mitochondria from atrophied and hypertrophied hearts. Metabolism. 2006;55:1097–1106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

