ESPRIT-Tree: hierarchical clustering analysis of millions of 16S rRNA pyrosequences in quasilinear computational time
- PMID: 21596775
- PMCID: PMC3152367
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr349
ESPRIT-Tree: hierarchical clustering analysis of millions of 16S rRNA pyrosequences in quasilinear computational time
Abstract
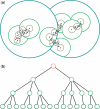
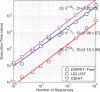
Taxonomy-independent analysis plays an essential role in microbial community analysis. Hierarchical clustering is one of the most widely employed approaches to finding operational taxonomic units, the basis for many downstream analyses. Most existing algorithms have quadratic space and computational complexities, and thus can be used only for small or medium-scale problems. We propose a new online learning-based algorithm that simultaneously addresses the space and computational issues of prior work. The basic idea is to partition a sequence space into a set of subspaces using a partition tree constructed using a pseudometric, then recursively refine a clustering structure in these subspaces. The technique relies on new methods for fast closest-pair searching and efficient dynamic insertion and deletion of tree nodes. To avoid exhaustive computation of pairwise distances between clusters, we represent each cluster of sequences as a probabilistic sequence, and define a set of operations to align these probabilistic sequences and compute genetic distances between them. We present analyses of space and computational complexity, and demonstrate the effectiveness of our new algorithm using a human gut microbiota data set with over one million sequences. The new algorithm exhibits a quasilinear time and space complexity comparable to greedy heuristic clustering algorithms, while achieving a similar accuracy to the standard hierarchical clustering algorithm.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ESPRIT-Forest: Parallel clustering of massive amplicon sequence data in subquadratic time.PLoS Comput Biol. 2017 Apr 24;13(4):e1005518. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005518. eCollection 2017 Apr. PLoS Comput Biol. 2017. PMID: 28437450 Free PMC article.
-
CLUSTOM-CLOUD: In-Memory Data Grid-Based Software for Clustering 16S rRNA Sequence Data in the Cloud Environment.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 8;11(3):e0151064. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151064. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26954507 Free PMC article.
-
A large-scale benchmark study of existing algorithms for taxonomy-independent microbial community analysis.Brief Bioinform. 2012 Jan;13(1):107-21. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbr009. Epub 2011 Apr 27. Brief Bioinform. 2012. PMID: 21525143 Free PMC article.
-
hc-OTU: A Fast and Accurate Method for Clustering Operational Taxonomic Units Based on Homopolymer Compaction.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2018 Mar-Apr;15(2):441-451. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2016.2535326. Epub 2016 Feb 26. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2018. PMID: 26930691
-
HCsnip: An R Package for Semi-supervised Snipping of the Hierarchical Clustering Tree.Cancer Inform. 2015 Mar 22;14:1-19. doi: 10.4137/CIN.S22080. eCollection 2015. Cancer Inform. 2015. PMID: 25861213 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intricacies of assessing the human microbiome in epidemiologic studies.Ann Epidemiol. 2016 May;26(5):311-21. doi: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2016.04.005. Epub 2016 Apr 12. Ann Epidemiol. 2016. PMID: 27180112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of malnutrition on norovirus infection.mBio. 2014 Mar 4;5(2):e01032-13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01032-13. mBio. 2014. PMID: 24595373 Free PMC article.
-
OptiClust, an Improved Method for Assigning Amplicon-Based Sequence Data to Operational Taxonomic Units.mSphere. 2017 Mar 8;2(2):e00073-17. doi: 10.1128/mSphereDirect.00073-17. eCollection 2017 Mar-Apr. mSphere. 2017. PMID: 28289728 Free PMC article.
-
Marine Oxygen-Deficient Zones Harbor Depauperate Denitrifying Communities Compared to Novel Genetic Diversity in Coastal Sediments.Microb Ecol. 2015 Aug;70(2):311-21. doi: 10.1007/s00248-015-0582-y. Epub 2015 Feb 28. Microb Ecol. 2015. PMID: 25721726
-
TBC: a clustering algorithm based on prokaryotic taxonomy.J Microbiol. 2012 Apr;50(2):181-5. doi: 10.1007/s12275-012-1214-6. Epub 2012 Apr 27. J Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22538644
References
-
- Fabrice A, Didier R. Exploring microbial diversity using 16S rRNA high-throughput methods. J. Comput. Sci. Syst. Biol. 2009;2:74–92.

