Bioinformatics challenges for personalized medicine
- PMID: 21596790
- PMCID: PMC3117361
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr295
Bioinformatics challenges for personalized medicine
Erratum in
- Bioinformatics. 2011 Aug 15;27(16):2323
Abstract
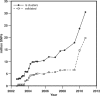
Motivation: Widespread availability of low-cost, full genome sequencing will introduce new challenges for bioinformatics.
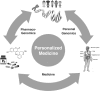
Results: This review outlines recent developments in sequencing technologies and genome analysis methods for application in personalized medicine. New methods are needed in four areas to realize the potential of personalized medicine: (i) processing large-scale robust genomic data; (ii) interpreting the functional effect and the impact of genomic variation; (iii) integrating systems data to relate complex genetic interactions with phenotypes; and (iv) translating these discoveries into medical practice.
Contact: russ.altman@stanford.edu
Figures
References
-
- Adie E.A., et al. SUSPECTS: enabling fast and effective prioritization of positional candidates. Bioinformatics. 2006;22:773–774. - PubMed
-
- Alexiou P., et al. Lost in translation: an assessment and perspective for computational microRNA target identification. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:3049–3055. - PubMed
-
- Altschul S.F., et al. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

