Chromatin "prepattern" and histone modifiers in a fate choice for liver and pancreas
- PMID: 21596989
- PMCID: PMC3128430
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1202845
Chromatin "prepattern" and histone modifiers in a fate choice for liver and pancreas
Abstract
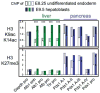
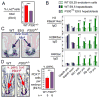
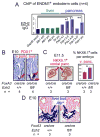
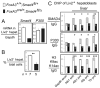
Transcriptionally silent genes can be marked by histone modifications and regulatory proteins that indicate the genes' potential to be activated. Such marks have been identified in pluripotent cells, but it is unknown how such marks occur in descendant, multipotent embryonic cells that have restricted cell fate choices. We isolated mouse embryonic endoderm cells and assessed histone modifications at regulatory elements of silent genes that are activated upon liver or pancreas fate choices. We found that the liver and pancreas elements have distinct chromatin patterns. Furthermore, the histone acetyltransferase P300, recruited via bone morphogenetic protein signaling, and the histone methyltransferase Ezh2 have modulatory roles in the fate choice. These studies reveal a functional "prepattern" of chromatin states within multipotent progenitors and potential targets to modulate cell fate induction.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

