Fibrocytes: emerging effector cells in chronic inflammation
- PMID: 21597472
- PMCID: PMC3599774
- DOI: 10.1038/nri2990
Fibrocytes: emerging effector cells in chronic inflammation
Abstract
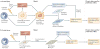
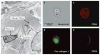
Fibrocytes are mesenchymal cells that arise from monocyte precursors. They are present in injured organs and have both the inflammatory features of macrophages and the tissue remodelling properties of fibroblasts. Chronic inflammatory stimuli mediate the differentiation, trafficking and accumulation of these cells in fibrosing conditions associated with autoimmunity, cardiovascular disease and asthma. This Opinion article discusses the immunological mediators controlling fibrocyte differentiation and recruitment, describes the association of fibrocytes with chronic inflammatory diseases and compares the potential roles of fibrocytes in these disorders with those of macrophages and fibroblasts. It is hoped that this information prompts new opportunities for the study of these unique cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests: see Web version for details.
Figures


References
-
- Cohnheim J. Ueber Entzundung und Eiterung (About inflammation and suppuration) Path Anat Physiol Klin Med. 1867;40:1–79.
-
- Chesney J, Metz C, Stavitsky AB, Bacher M, Bucala R. Regulated production of type I collagen and inflammatory cytokines by peripheral blood fibrocytes. J Immunol. 1998;160:419–425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

