Generation of a monoclonal antibody reactive to prefusion myocytes
- PMID: 21597958
- PMCID: PMC3141826
- DOI: 10.1007/s10974-011-9247-8
Generation of a monoclonal antibody reactive to prefusion myocytes
Abstract
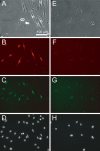
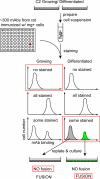
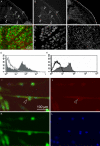
We established a novel monoclonal antibody, Yaksa that is specific to a subpopulation of myogenic cells. The Yaksa antigen is not expressed on the surface of growing myoblasts but only on a subpopulation of myogenin-positive myocytes. When Yaksa antigen-positive mononucleated cells were freshly prepared from a murine myogenic cell by a cell sorter, they fused with each other and formed multinucleated myotubes shortly after replating while Yaksa antigen-negative cells scarcely generated myotubes. These results suggest that Yaksa could segregate fusion-competent, mononucleated cells from fusion-incompetent cells during muscle differentiation. The Yaksa antigen was also expressed in developing muscle and regenerating muscle in vivo and it was localized at sites of cell-cell contact between mono-nucleated muscle cells and between mono-nucleated muscle cells and myotubes. Thus, Yaksa that marks prefusion myocytes before myotube formation can be a useful tool to elucidate the cellular and molecular mechanisms of myogenic cell fusion.
Figures