Effects of intermittent parathyroid hormone treatment on osteoprogenitor cells in postmenopausal women
- PMID: 21600325
- PMCID: PMC3143310
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2011.05.003
Effects of intermittent parathyroid hormone treatment on osteoprogenitor cells in postmenopausal women
Abstract
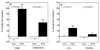
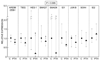
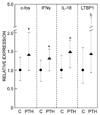
Intermittent parathyroid hormone (PTH) 1-34 treatment stimulates bone formation, but the molecular mechanisms mediating this effect have not been previously studied in humans. Thus, we used magnetic activated cell sorting to isolate hematopoietic lineage negative (lin-)/alkaline phosphatase positive (AP+) osteoprogenitor cells from bone marrow of 20 postmenopausal women treated with PTH (1-34) for 14 days and 19 control subjects. Serum PINP and CTX increased in PTH-treated subjects (by 97% and 30%, respectively, P<0.001). Bone marrow lin-/AP+ cells from PTH-treated subjects showed an increase in the RANKL/OPG mRNA ratio (by 7.5-fold, P=0.011) and in the mRNAs for c-fos (a known PTH-responsive gene, by 42%, P=0.035) and VEGF-C (by 57%, P=0.046). Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA, testing for changes in pre-specified pathways) demonstrated that PTH had no effect on osteoblast proliferation, apoptosis, or differentiation markers. However, PTH treatment resulted in a significant decrease (GSEA P-value, 0.005) in a panel of BMP target genes in the lin-/AP+ cells. Our findings thus identify several future directions for studying mechanisms of PTH action in humans. First, given the increasing evidence that PTH induces angiogenesis, the role of increased VEGF-C production by bone marrow osteoprogenitor cells in mediating this effect and the anabolic response to PTH warrants further study. Second, while the observed inhibition of BMP target gene expression by PTH is not consistent with the anabolic effects of PTH on bone and requires further validation, these data do generate the hypothesis that an inhibition of BMP signaling by PTH may, over time, limit the availability of mature osteoblasts on bone surfaces and thereby contribute to the observed waning of the anabolic response to PTH.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Neer RM, Arnaud CD, Zanchetta JR, Prince R, Gaich GA, Reginster JY, Hodsman AB, Eriksen EF, Ish-Shalom S, Genant HK, Wang O, Mitlak BH. Effect of parathyroid hormone (1–34) on fractures and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1434–1441. - PubMed
-
- Dempster DW, Cosman F, Kurland ES, Zhou H, Nieves J, Woelfert L, Shane E, Plavetic K, Muller R, Bilezikian J, Lindsay R. Effects of daily treatment with parathyroid hormone on bone microarchitecture and turnover in patients with osteoporosis: a paired biopsy study. J Bone Miner Res. 2001;16:1846–1853. - PubMed
-
- Lindsay R, Zhou H, Cosman F, Nieves J, Dempster DW, Hodsman AB. Effects if a one-month treatment with PTH(1–34) on bone formation on cancellous, endocortical, and periosteal surfaces of the human ilium. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22:495–502. - PubMed
-
- Li X, Liu H, Qin L, Tamasi J, Bergenstock M, Shapses S, Feyen JHM, Notterman DA, Partridge NC. Determination of dual effects of parathyroid hormone on skeletal gene expression in vivo by mircoarray and network analysis. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:33086–33097. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

