Regulating SR protein phosphorylation through regions outside the kinase domain of SRPK1
- PMID: 21600902
- PMCID: PMC3121894
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.04.077
Regulating SR protein phosphorylation through regions outside the kinase domain of SRPK1
Erratum in
- J Mol Biol. 2011 Aug 12;411(2):511. Whitehouse, Jennifer [corrected to Whitesides, Jennifer]
Abstract
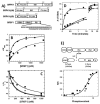
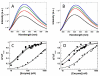
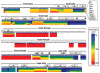
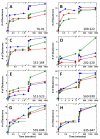
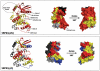
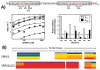
SR proteins (splicing factors containing arginine-serine repeats) are essential splicing factors whose phosphorylation by the SR-specific protein kinase (SRPK) family regulates nuclear localization and mRNA processing activity. In addition to an N-terminal extension with unknown function, SRPKs contain a large, nonhomologous spacer insert domain (SID) that bifurcates the kinase domain and anchors the kinase in the cytoplasm through interactions with chaperones. While structures for the kinase domain are now available, constructs that include regions outside this domain have been resistant to crystallographic elucidation. To investigate the conformation of the full-length kinase and the functional role of noncatalytic regions, we performed hydrogen-deuterium exchange and steady-state kinetic experiments on SRPK1. Unlike the kinase core, the large SID lacks stable, hydrogen-bonded structure and may provide an intrinsically disordered region for chaperone interactions. Conversely, the N-terminus, which positively regulates SR protein binding, adopts a stable structure when the insert domain is present and stabilizes a docking groove in the large lobe of the kinase domain. The N-terminus and SID equally enhance SR protein turnover by altering the stability of several catalytic loop segments. These studies reveal that SRPK1 uses an N-terminal extension and a large, intrinsically disordered region juxtaposed to a stable structure to facilitate high-affinity SR protein interactions and phosphorylation rates.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI081982/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM020501/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR029388/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- GM090484/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI076961/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- GM67969/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM020501/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007752/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R33 CA099835/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM066170/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS070899/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AI076961/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA118595/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA099835/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI081982/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA118595/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA099835/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM093325/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM093325/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM090484/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM020501/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM066170/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AI2008031/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR029388/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM067969/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

