Engineering Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) derivative strains to minimize E. coli protein contamination after purification by immobilized metal affinity chromatography
- PMID: 21602383
- PMCID: PMC3127686
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00119-11
Engineering Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) derivative strains to minimize E. coli protein contamination after purification by immobilized metal affinity chromatography
Erratum in
-
Erratum for Robichon et al., "Engineering Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) Derivative Strains To Minimize E. coli Protein Contamination after Purification by Immobilized Metal Affinity Chromatography".Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023 Nov 29;89(11):e0161623. doi: 10.1128/aem.01616-23. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37889015 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
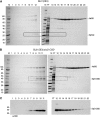
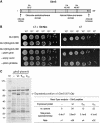
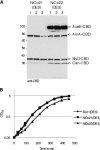
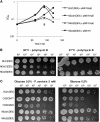
Recombinant His-tagged proteins expressed in Escherichia coli and purified by immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC) are commonly coeluted with native E. coli proteins, especially if the recombinant protein is expressed at a low level. The E. coli contaminants display high affinity to divalent nickel or cobalt ions, mainly due to the presence of clustered histidine residues or biologically relevant metal binding sites. To improve the final purity of expressed His-tagged protein, we engineered E. coli BL21(DE3) expression strains in which the most recurring contaminants are either expressed with an alternative tag or mutated to decrease their affinity to divalent cations. The current study presents the design, engineering, and characterization of two E. coli BL21(DE3) derivatives, NiCo21(DE3) and NiCo22(DE3), which express the endogenous proteins SlyD, Can, ArnA, and (optionally) AceE fused at their C terminus to a chitin binding domain (CBD) and the protein GlmS, with six surface histidines replaced by alanines. We show that each E. coli CBD-tagged protein remains active and can be efficiently eliminated from an IMAC elution fraction using a chitin column flowthrough step, while the modification of GlmS results in loss of affinity for nickel-containing resin. The "NiCo" strains uniquely complement existing methods for improving the purity of recombinant His-tagged protein.
Figures


References
-
- Abdel-Hamid A. M., Attwood M. M., Guest J. R. 2001. Pyruvate oxidase contributes to the aerobic growth efficiency of Escherichia coli. Microbiology 147:1483–1498 - PubMed
-
- Arnold F. H. 1991. Metal-affinity separations: a new dimension in protein processing. Biotechnology (N. Y.) 9:151–156 - PubMed
-
- Bolanos-Garcia V. M., Davies O. R. 2006. Structural analysis and classification of native proteins from E. coli commonly co-purified by immobilised metal affinity chromatography. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1760:1304–1313 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

