Development and application of a cellular, gain-of-signal, bioluminescent reporter screen for inhibitors of type II secretion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia pseudomallei
- PMID: 21602485
- PMCID: PMC3195541
- DOI: 10.1177/1087057111408605
Development and application of a cellular, gain-of-signal, bioluminescent reporter screen for inhibitors of type II secretion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia pseudomallei
Abstract
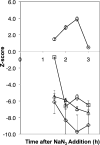
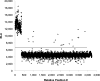
The type II secretion (T2S) system in gram-negative bacteria comprises the Sec and Tat pathways for translocating proteins into the periplasm and an outer membrane secretin for transporting proteins into the extracellular space. To discover Sec/Tat/T2S pathway inhibitors as potential new therapeutics, the authors used a Pseudomonas aeruginosa bioluminescent reporter strain responsive to SecA depletion and inhibition to screen compound libraries and characterize the hits. The reporter strain placed a luxCDABE operon under regulation of a SecA depletion-responsive upregulated promoter in a secA deletion background complemented with an ectopic lac-regulated secA copy. Bioluminescence was indirectly proportional to the isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside concentration and stimulated by azide, a known SecA ATPase inhibitor. A total of 96 compounds (0.1% of 73,000) were detected as primary hits due to stimulation of luminescence with a z score ≥5. Direct secretion assays of the nine most potent hits, representing five chemical scaffolds, revealed that they do not inhibit SecA-mediated secretion of β-lactamase into the periplasm but do inhibit T2S-mediated extracellular secretion of elastase with IC(50) values from 5 to 25 µM. In addition, seven of the nine compounds also inhibited the T2S-mediated extracellular secretion of phospholipase C by P. aeruginosa and protease activity by Burkholderia pseudomallei.
Figures



References
-
- McGowan JE., Jr Resistance in nonfermenting gram-negative bacteria: multidrug resistance to the maximum. Am J Infect Control. 2006;34:S29–37. discussion S64–73. - PubMed
-
- Mentzelopoulos SD, Pratikaki M, Platsouka E, Kraniotaki H, Zervakis D, Koutsoukou A, Nanas S, Paniara O, Roussos C, Giamarellos-Bourboulis E, Routsi C, Zakynthinos SG. Prolonged use of carbapenems and colistin predisposes to ventilator-associated pneumonia by pandrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Intensive Care Med. 2007;33:1524–1532. - PubMed
-
- den Blaauwen T, Driessen AJ. Sec-dependent preprotein translocation in bacteria. Arch Microbiol. 1996;165:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Filloux A. The underlying mechanisms of type II protein secretion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1694:163–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

