Impaired insulin secretion and enhanced insulin sensitivity in cholecystokinin-deficient mice
- PMID: 21602512
- PMCID: PMC3121422
- DOI: 10.2337/db10-0789
Impaired insulin secretion and enhanced insulin sensitivity in cholecystokinin-deficient mice
Abstract
Objective: Cholecystokinin (CCK) is released in response to lipid intake and stimulates insulin secretion. We hypothesized that CCK deficiency would alter the regulation of insulin secretion and glucose homeostasis.
Research design and methods: We used quantitative magnetic resonance imaging to determine body composition and studied plasma glucose and insulin secretion of CCK gene knockout (CCK-KO) mice and their wild-type controls using intraperitoneal glucose and arginine infusions. The area of anti-insulin staining in pancreatic islets was measured by immunohistochemistry. Insulin sensitivity was assessed with euglycemic-hyperinsulemic clamps.
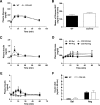
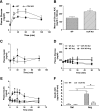
Results: CCK-KO mice fed a low-fat diet had a reduced acute insulin response to glucose but a normal response to arginine and normal glucose tolerance, associated with a trend toward greater insulin sensitivity. However, when fed a high-fat diet (HFD) for 10 weeks, CCK-KO mice developed glucose intolerance despite increased insulin sensitivity that was associated with low insulin secretion in response to both glucose and arginine. The deficiency of insulin secretion in CCK-KO mice was not associated with changes in β-cell or islet size.
Conclusions: CCK is involved in regulating insulin secretion and glucose tolerance in mice eating an HFD. The impaired insulin response to intraperitoneal stimuli that do not typically elicit CCK release suggests that this hormone has chronic effects on β-cell adaptation to diet in addition to acute incretin actions.
© 2011 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cholecystokinin knockout mice are resistant to high-fat diet-induced obesity.Gastroenterology. 2010 May;138(5):1997-2005. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.01.044. Epub 2010 Feb 1. Gastroenterology. 2010. PMID: 20117110 Free PMC article.
-
Energy homeostasis in apolipoprotein AIV and cholecystokinin-deficient mice.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2017 Nov 1;313(5):R535-R548. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00034.2017. Epub 2017 Aug 2. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28768657 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Id1 augments insulin secretion and protects against high-fat diet-induced glucose intolerance.Diabetes. 2011 Oct;60(10):2506-14. doi: 10.2337/db11-0083. Epub 2011 Sep 22. Diabetes. 2011. PMID: 21940780 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Effects of Selective Deletion of Group VIA Phospholipase A2 from Macrophages or Pancreatic Islet Beta-Cells.Biomolecules. 2020 Oct 17;10(10):1455. doi: 10.3390/biom10101455. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 33080873 Free PMC article.
-
A beta cell ATGL-lipolysis/adipose tissue axis controls energy homeostasis and body weight via insulin secretion in mice.Diabetologia. 2016 Dec;59(12):2654-2663. doi: 10.1007/s00125-016-4105-2. Epub 2016 Sep 27. Diabetologia. 2016. PMID: 27677764 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Quantitation and chemical coding of enteroendocrine cell populations in the human jejunum.Cell Tissue Res. 2020 Jan;379(1):109-120. doi: 10.1007/s00441-019-03099-3. Epub 2019 Sep 2. Cell Tissue Res. 2020. PMID: 31478137 Free PMC article.
-
Inferring causal pathways among three or more variables from steady-state correlations in a homeostatic system.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 11;13(10):e0204755. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204755. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30307959 Free PMC article.
-
Corydalis edulis Maxim. Promotes Insulin Secretion via the Activation of Protein Kinase Cs (PKCs) in Mice and Pancreatic β Cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 16;7:40454. doi: 10.1038/srep40454. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28091547 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the metabolic effects of sustained CCK1 receptor activation alone and in combination with upregulated leptin signalling in high-fat-fed mice.Diabetologia. 2013 Jun;56(6):1425-35. doi: 10.1007/s00125-013-2878-0. Epub 2013 Mar 6. Diabetologia. 2013. PMID: 23462797
-
Apolipoprotein A4 Elevates Sympathetic Activity and Thermogenesis in Male Mice.Nutrients. 2023 May 26;15(11):2486. doi: 10.3390/nu15112486. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37299447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hampton SM, Kwasowski P, Tan K, Morgan LM, Marks V. Effect of pretreatment with a high fat diet on the gastric inhibitory polypeptide and insulin responses to oral triolein and glucose in rats. Diabetologia 1983;24:278–281 - PubMed
-
- Liddle RA, Goldfine ID, Williams JA. Bioassay of plasma cholecystokinin in rats: effects of food, trypsin inhibitor, and alcohol. Gastroenterology 1984;87:542–549 - PubMed
-
- Reimer MK, Holst JJ, Ahrén B. Long-term inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV improves glucose tolerance and preserves islet function in mice. Eur J Endocrinol 2002;146:717–727 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK-56863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-078283/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK59630/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK056863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059630/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK017844/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-72968/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-70992/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK078283/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-83550/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK070992/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK017844/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK083550/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-17844/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

