Genome-wide association and linkage identify modifier loci of lung disease severity in cystic fibrosis at 11p13 and 20q13.2
- PMID: 21602797
- PMCID: PMC3296486
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.838
Genome-wide association and linkage identify modifier loci of lung disease severity in cystic fibrosis at 11p13 and 20q13.2
Abstract
A combined genome-wide association and linkage study was used to identify loci causing variation in cystic fibrosis lung disease severity. We identified a significant association (P = 3.34 × 10(-8)) near EHF and APIP (chr11p13) in p.Phe508del homozygotes (n = 1,978). The association replicated in p.Phe508del homozygotes (P = 0.006) from a separate family based study (n = 557), with P = 1.49 × 10(-9) for the three-study joint meta-analysis. Linkage analysis of 486 sibling pairs from the family based study identified a significant quantitative trait locus on chromosome 20q13.2 (log(10) odds = 5.03). Our findings provide insight into the causes of variation in lung disease severity in cystic fibrosis and suggest new therapeutic targets for this life-limiting disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing financial interests.
Figures
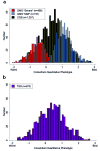


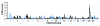

Comment in
-
New modifier loci in cystic fibrosis.Nat Genet. 2011 Jun;43(6):508-9. doi: 10.1038/ng.844. Nat Genet. 2011. PMID: 21614089 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hamosh A, Corey M. Correlation between genotype and phenotype in patients with cystic fibrosis. The Cystic Fibrosis Genotype-Phenotype Consortium. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:1308–1313. - PubMed
-
- Chalmers JD, Fleming GB, Hill AT, Kilpatrick DC. Impact of mannose binding lectin (MBL) insufficiency on the course of cystic fibrosis: a review and meta-analysis. Glycobiology. 2010 - PubMed
-
- Corey M, Edwards L, Levison H, Knowles M. Longitudinal analysis of pulmonary function decline in patients with cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr. 1997;131:809–814. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R03 HG004314/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL068890/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK027651/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- P30 DK027651/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL072748/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL068927/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095396/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH059490/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK066368/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL068890/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23DK083551/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK083551/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK066368/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL095396/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059490/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL068927/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HG-0004314/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- MH059490/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

