Iduna protects the brain from glutamate excitotoxicity and stroke by interfering with poly(ADP-ribose) polymer-induced cell death
- PMID: 21602803
- PMCID: PMC3709257
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2387
Iduna protects the brain from glutamate excitotoxicity and stroke by interfering with poly(ADP-ribose) polymer-induced cell death
Abstract
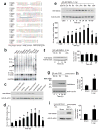
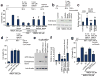
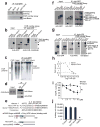
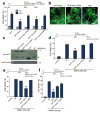
Glutamate acting on N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors induces neuronal injury following stroke, through activation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) and generation of the death molecule poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) polymer. Here we identify Iduna, a previously undescribed NMDA receptor-induced survival protein that is neuroprotective against glutamate NMDA receptor-mediated excitotoxicity both in vitro and in vivo and against stroke through interfering with PAR polymer-induced cell death (parthanatos). Iduna's protective effects are independent and downstream of PARP-1 activity. Iduna is a PAR polymer-binding protein, and mutation at the PAR polymer binding site abolishes the PAR binding activity of Iduna and attenuates its protective actions. Iduna is protective in vivo against NMDA-induced excitotoxicity and middle cerebral artery occlusion-induced stroke in mice. To our knowledge, these results define Iduna as the first known endogenous inhibitor of parthanatos. Interfering with PAR polymer signaling could be a new therapeutic strategy for the treatment of neurologic disorders.
Figures

References
-
- Aarts MM, Tymianski M. Molecular mechanisms underlying specificity of excitotoxic signaling in neurons. Curr Mol Med. 2004;4:137–147. - PubMed
-
- Waxman EA, Lynch DR. N-methyl-D-aspartate Receptor Subtypes: Multiple Roles in Excitotoxicity and Neurological Disease. Neuroscientist. 2005;11:37–49. - PubMed
-
- Yu SW, Wang H, Dawson TM, Dawson VL. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 and apoptosis inducing factor in neurotoxicity. Neurobiol Dis. 2003;14:303–317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

