High intensity focused ultrasound in clinical tumor ablation
- PMID: 21603311
- PMCID: PMC3095464
- DOI: 10.5306/wjco.v2.i1.8
High intensity focused ultrasound in clinical tumor ablation
Abstract
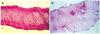
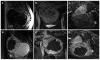
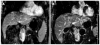
Recent advances in high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), which was developed in the 1940s as a viable thermal tissue ablation approach, have increased its popularity. In clinics, HIFU has been applied to treat a variety of solid malignant tumors in a well-defined volume, including the pancreas, liver, prostate, breast, uterine fibroids, and soft-tissue sarcomas. In comparison to conventional tumor/cancer treatment modalities, such as open surgery, radio- and chemo-therapy, HIFU has the advantages of non-invasion, non-ionization, and fewer complications after treatment. Over 100 000 cases have been treated throughout the world with great success. The fundamental principles of HIFU ablation are coagulative thermal necrosis due to the absorption of ultrasound energy during transmission in tissue and the induced cavitation damage. This paper reviews the clinical outcomes of HIFU ablation for applicable cancers, and then summarizes the recommendations for a satisfactory HIFU treatment according to clinical experience. In addition, the current challenges in HIFU for engineers and physicians are also included. More recent horizons have broadened the application of HIFU in tumor treatment, such as HIFU-mediated drug delivery, vessel occlusion, and soft tissue erosion ("histotripsy"). In summary, HIFU is likely to play a significant role in the future oncology practice.
Keywords: Bioeffects; Bubble cavitation; Cancer; High intensity focused ultrasound; Image-guided therapy; Thermal ablation.
Figures



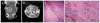

References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59:225–249. - PubMed
-
- The Freedonia Group. Cancer therapies to 2009 - Market research, market share, market size, sales, demand forecast, market leaders, company profiles, industry trends, 2009
-
- ter Haar G, Rivens I, Chen L, Riddler S. High intensity focused ultrasound for the treatment of rat tumours. Phys Med Biol. 1991;36:1495–1501. - PubMed
-
- Gelet A, Chapelon JY, Bouvier R, Rouvière O, Lasne Y, Lyonnet D, Dubernard JM. Transrectal high-intensity focused ultrasound: minimally invasive therapy of localized prostate cancer. J Endourol. 2000;14:519–528. - PubMed
-
- Visioli AG, Rivens IH, ter Haar GR, Horwich A, Huddart RA, Moskovic E, Padhani A, Glees J. Preliminary results of a phase I dose escalation clinical trial using focused ultrasound in the treatment of localised tumours. Eur J Ultrasound. 1999;9:11–18. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

