Imaging of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors
- PMID: 21603312
- PMCID: PMC3095463
- DOI: 10.5306/wjco.v2.i1.28
Imaging of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors
Abstract
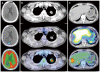
Imaging of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors can be broadly divided into anatomic and functional techniques. Anatomic imaging determines the local extent of the primary lesion, providing crucial information required for surgical planning. Functional imaging, not only determines the extent of metastatic disease spread, but also provides important information with regard to the biologic behavior of the tumor, allowing clinicians to decide on the most appropriate forms of treatment. We review the current literature on this subject, with emphasis on the strengths of each imaging modality.
Keywords: Magnetic resonance imaging; Neuroendocrine tumor; Positron emission tomography; Somatostatin receptor scintigraphy.
Figures


References
-
- Lubarsch O. Ueber den primären krebs des ileum nebst bemerkungen über das gleichzeitige vorkommen von krebs und tuberculose. Virchows Arch Pathol Anat. 1888;111:280–317.
-
- Feyrter F. Über diffuse endokrine epitheliale Organe. Zentralblatt Innere Medizin. 1938;59:546–556.
-
- Langley K. The neuroendocrine concept today. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994;733:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Said JW, Vimadalal S, Nash G, Shintaku IP, Heusser RC, Sassoon AF, Lloyd RV. Immunoreactive neuron-specific enolase, bombesin, and chromogranin as markers for neuroendocrine lung tumors. Hum Pathol. 1985;16:236–240. - PubMed
-
- Hainsworth JD, Wright EP, Johnson DH, Davis BW, Greco FA. Poorly differentiated carcinoma of unknown primary site: clinical usefulness of immunoperoxidase staining. J Clin Oncol. 1991;9:1931–1938. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

