Infliximab-associated Chiasmopathy
Abstract
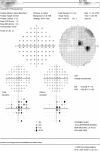
Optic neuropathy has been reported in association with the use of tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonists such as etanercept, infliximab, and adalimumab. This is a report of a patient who began experiencing decreased vision approximately 1 month after starting infliximab therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Visual field testing showed bitemporal hemianopic scotomas, indicating involvement of the nerve fibers in the optic chiasm. The infliximab was discontinued, and the patient experienced substantial improvement in her visual acuity and visual field.
Keywords: infliximab; optic neuropathy.
Figures
References
-
- van Oosten B. W., Barkhof F., Truyen L., et al. Increased MRI activity and immune reaction in two multiple sclerosis patients treated with the monoclonal anti-tumor necrosis factor antibody cA2. Neurology. 1996;47:1531–1534. - PubMed
-
- Sacks J. G., Melen O. Bitemporal visual field defects in presumed multiple sclerosis. JAMA. 1975;234:69–72. - PubMed
-
- Foroozan R., Buono L. M., Sergott R. C., Savino P. J. Retrobulbar optic neuritis associated with infliximab. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002;120:985–987. - PubMed
-
- The Lenercept Multiple Sclerosis Study Group and The University of British Columbia MS/MRI Analysis Group. TNF neutralization in MS: Results of a randomized, placebo-controlled multicenter study. Neurology. 1995;53:457–465. - PubMed
-
- Strong B. Y., Enry B. C., Herzenberg H., Razzeca K. J. Retrobulbar optic neuritis associated with infliximab in a patient with Crohn Disease. Ann Intern Med. 2004;20:140:E678. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources