Oral GABA treatment downregulates inflammatory responses in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 21604972
- PMCID: PMC5787624
- DOI: 10.3109/08916934.2011.571223
Oral GABA treatment downregulates inflammatory responses in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
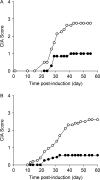
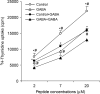
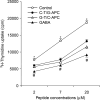
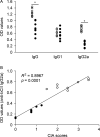
Current treatments for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) have long-term side effects such that new treatments are needed that can safely help manage the disease. There is a growing appreciation that GABA receptors (GABA-Rs) on immune cells provide new targets that can be used to modulate immune cell activity. Here, we show for the first time that activation of peripheral GABA-Rs can inhibit the development of disease in the collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mouse model of RA. Mice that received oral GABA had a reduced incidence of CIA, and those mice that did develop CIA had milder symptoms. T cells from GABA-treated mice displayed reduced proliferative responses to collagen and their APC had a reduced ability to promote the proliferation of collagen-reactive T cells. Thus, GABA downregulated both T-cell autoimmunity and APC activity. Collagen-reactive T cells from GABA-treated mice displayed reduced recall responses in the presence of GABA ex vivo, indicating that GABA consumption did not desensitize these cells to GABA. GABA-treated mice had reduced collagen-reactive IgG2a, but not IgG1 antibodies, consistent with reduced Th1 help. The levels of serum anti-collagen IgG2a antibodies were correlated significantly with the CIA disease scores of individual mice. Our results suggest that activation of peripheral GABA-Rs may provide a new modality to modulate T cell, B cell, and APC activity and help ameliorate RA and other inflammatory diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
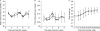
References
-
- Erdo SL, Wolff JR. Gamma-aminobutyric acid outside the mammalian brain. J Neurochem. 1990;54:363–372. - PubMed
-
- Tian J, Chau C, Hales TG, Kaufman DL. GABA(A) receptors mediate inhibition of T cell responses. J Neuroimmunol. 1999;96:21–28. - PubMed
-
- Tian J, Lu Y, Zhang H, Chau CH, Dang HN, Kaufman DL. Gamma-aminobutyric acid inhibits T cell autoimmunity and the development of inflammatory responses in a mouse type 1 diabetes model. J Immunol. 2004;173:5298–5304. - PubMed
-
- Bergeret M, Khrestchatisky M, Tremblay E, Bernard A, Gregoire A, Chany C. GABA modulates cytotoxicity of immunocompetent cells expressing GABAA receptor subunits. Biomed Pharmacother. 1998;52:214–219. - PubMed
-
- Reyes-Garcia MG, Hernandez-Hernandez F, Hernandez-Tellez B, Garcia-Tamayo F. GABA(A) receptor subunits RNA expression in mice peritoneal macrophages modulate their IL-6/IL-12 production. J Neuroimmunol. 2007;188:64–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
