Transmission probabilities and durations of immunity for three pathogenic group B Streptococcus serotypes
- PMID: 21605704
- PMCID: PMC3391980
- DOI: 10.1016/j.meegid.2011.05.005
Transmission probabilities and durations of immunity for three pathogenic group B Streptococcus serotypes
Abstract
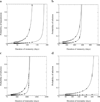
Group B Streptococcus (GBS) remains a major cause of neonatal sepsis and is an emerging cause of invasive bacterial infections. The 9 known serotypes vary in virulence, and there is little cross-immunity. Key parameters for planning an effective vaccination strategy, such as average length of immunity and transmission probabilities by serotype, are unknown. We simulated GBS spread in a population using a computational model with parameters derived from studies of GBS sexual transmission in a college dormitory. Here we provide estimates of the duration of immunity relative to the transmission probabilities for the 3 GBS serotypes most associated with invasive disease: Ia, III, and V. We also place upper limits on the durations of immunity for serotype Ia (570 days), III (1125 days) and V (260 days). Better transmission estimates are required to establish the epidemiological parameters of GBS infection and determine the best vaccination strategies to prevent GBS disease.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
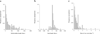
References
-
- Phares CR, Lynfield R, Farley MM, et al. Epidemiology of invasive group B streptococcal disease in the United States, 1999–2005. JAMA. 2008;299:2056–2065. - PubMed
-
- Schrag SJ, Zywicki S, Farley MM, et al. Group B streptococcal disease in the era of intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:15–20. - PubMed
-
- Baker CJ, Rench MA, Edwards MS, Carpenter RJ, Hays BM, Kasper DL. Immunization of pregnant women with a polysaccharide vaccine of group B streptococcus. N Engl J Med. 1988;319:1180–1185. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

