Diagnosis and clinical features of pemphigus foliaceus
- PMID: 21605805
- PMCID: PMC3108573
- DOI: 10.1016/j.det.2011.03.012
Diagnosis and clinical features of pemphigus foliaceus
Abstract
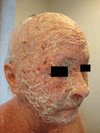
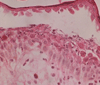
Pemphigus foliaceus is an acquired autoimmune blistering disease in which the body's immune system produces IgG autoantibodies that target the intercellular adhesion glycoprotein desmoglein-1, which is principally expressed in the granular layer of the epidermis, resulting in the loss of intercellular connections between keratinocytes (acantholysis) and the formation of subcorneal blisters within the epidermis. This article summarizes the epidemiology, clinical features, techniques for diagnosis, and drugs associated with treatment of this rare disease.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this paper have no financial disclosures or conflicts of interest to express.
Figures



References
-
- Rock B, Martins CR, Theofilopoulos AN, et al. The pathogenic effect of IgG4 autoantibodies in endemic pemphigus foliaceus (fogo selvagem) N Engl J Med. 1989;320:1463–1469. - PubMed
-
- Sekiguchi M, Futei Y, Fujii Y. Dominant autoimmune epitopes recognized by pemphigus antibodies map to the N-terminal adhesive region of desmogleins. J Immunol. 2001;167:5439–5448. - PubMed
-
- Rubenstein DS, Diaz LA. Pemphigus antibody induced phosphorylation of keratinocyte proteins. Autoimmunity. 2006;39:577–586. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

